Phytochemicals as an Alternative or Integrative Option, in Conjunction with Conventional Treatments for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 34830907
- PMCID: PMC8616323
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13225753
Phytochemicals as an Alternative or Integrative Option, in Conjunction with Conventional Treatments for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
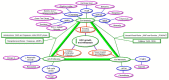
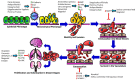
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most abundant form of liver cancer. It accounts for 75-85% of liver cancer cases and, though it ranks globally as the sixth most common cancer, it ranks second in cancer-related mortality. Deaths from HCC are usually due to metastatic spread of the cancer. Unfortunately, there are many challenges and limitations with the latest HCC therapies and medications, making it difficult for patients to receive life-prolonging care. As there is clearly a high demand for alternative therapy options for HCC, it is prudent to turn to plants for the solution, as their phytochemicals have long been used and revered for their many medicinal purposes. This review explores the promising phytochemical compounds identified from pre-clinical and clinical trials being used either independently or in conjunction with already existing cancer therapy treatments. The phytochemicals discussed in this review were classified into several categories: lipids, polyphenols, alkaloids, polysaccharides, whole extracts, and phytochemical combinations. Almost 80% of the compounds failed to progress into clinical studies due to lack of information regarding the toxicity to normal cells and bioavailability. Although large obstacles remain, phytochemicals can be used either as an alternative or integrative therapy in conjunction with existing HCC chemotherapies. In conclusion, phytochemicals have great potential as treatment options for hepatocellular carcinoma.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma; liver cancer; metastasis; natural compounds; phytochemicals.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

