Dynamic Role of Phospholipases A2 in Health and Diseases in the Central Nervous System
- PMID: 34831185
- PMCID: PMC8616333
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10112963
Dynamic Role of Phospholipases A2 in Health and Diseases in the Central Nervous System
Abstract
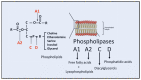
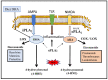
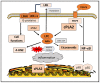
Phospholipids are major components in the lipid bilayer of cell membranes. These molecules are comprised of two acyl or alkyl groups and different phospho-base groups linked to the glycerol backbone. Over the years, substantial interest has focused on metabolism of phospholipids by phospholipases and the role of their metabolic products in mediating cell functions. The high levels of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) in the central nervous system (CNS) have led to studies centered on phospholipases A2 (PLA2s), enzymes responsible for cleaving the acyl groups at the sn-2 position of the phospholipids and resulting in production of PUFA and lysophospholipids. Among the many subtypes of PLA2s, studies have centered on three major types of PLA2s, namely, the calcium-dependent cytosolic cPLA2, the calcium-independent iPLA2 and the secretory sPLA2. These PLA2s are different in their molecular structures, cellular localization and, thus, production of lipid mediators with diverse functions. In the past, studies on specific role of PLA2 on cells in the CNS are limited, partly because of the complex cellular make-up of the nervous tissue. However, understanding of the molecular actions of these PLA2s have improved with recent advances in techniques for separation and isolation of specific cell types in the brain tissue as well as development of sensitive molecular tools for analyses of proteins and lipids. A major goal here is to summarize recent studies on the characteristics and dynamic roles of the three major types of PLA2s and their oxidative products towards brain health and neurological disorders.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; central nervous system; lysophospholipids; oxidized fatty acids; oxylipins; phospholipases A2; stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

