Zinc Ameliorates the Osteogenic Effects of High Glucose in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells
- PMID: 34831306
- PMCID: PMC8623153
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10113083
Zinc Ameliorates the Osteogenic Effects of High Glucose in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells
Abstract
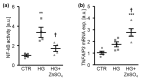
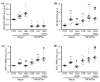
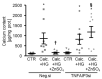
In diabetic patients, medial vascular calcification is common and associated with increased cardiovascular mortality. Excessive glucose concentrations can activate the nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B-cells (NF-kB) and trigger pro-calcific effects in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs), which may actively augment vascular calcification. Zinc is able to mitigate phosphate-induced VSMC calcification. Reduced serum zinc levels have been reported in diabetes mellitus. Therefore, in this study the effects of zinc supplementation were investigated in primary human aortic VSMCs exposed to excessive glucose concentrations. Zinc treatment was found to abrogate the stimulating effects of high glucose on VSMC calcification. Furthermore, zinc was found to blunt the increased expression of osteogenic and chondrogenic markers in high glucose-treated VSMCs. High glucose exposure was shown to activate NF-kB in VSMCs, an effect that was blunted by additional zinc treatment. Zinc was further found to increase the expression of TNFα-induced protein 3 (TNFAIP3) in high glucose-treated VSMCs. The silencing of TNFAIP3 was shown to abolish the protective effects of zinc on high glucose-induced NF-kB-dependent transcriptional activation, osteogenic marker expression, and the calcification of VSMCs. Silencing of the zinc-sensing receptor G protein-coupled receptor 39 (GPR39) was shown to abolish zinc-induced TNFAIP3 expression and the effects of zinc on high glucose-induced osteogenic marker expression. These observations indicate that zinc may be a protective factor during vascular calcification in hyperglycemic conditions.
Keywords: GPR39; NF-kB; diabetes mellitus; high glucose; osteogenic transition; vascular calcification; vascular smooth muscle cells; zinc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


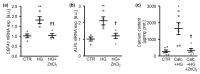
Similar articles
-
Zinc Inhibits Phosphate-Induced Vascular Calcification through TNFAIP3-Mediated Suppression of NF-κB.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018 Jun;29(6):1636-1648. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2017050492. Epub 2018 Apr 13. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 29654213 Free PMC article.
-
Role of SGK1 in the Osteogenic Transdifferentiation and Calcification of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells Promoted by Hyperglycemic Conditions.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 29;21(19):7207. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197207. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33003561 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of osteo/chondrogenic transformation of vascular smooth muscle cells by MgCl2 via calcium-sensing receptor.J Hypertens. 2017 Mar;35(3):523-532. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000001202. J Hypertens. 2017. PMID: 27984337
-
Copper Impedes Calcification of Human Aortic Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells Through Inhibition of Osteogenic Transdifferentiation and Promotion of Extracellular Matrix Stability.J Cell Physiol. 2025 Apr;240(4):e70035. doi: 10.1002/jcp.70035. J Cell Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40249000 Free PMC article.
-
Zinc Action in Vascular Calcification.Prev Nutr Food Sci. 2024 Jun 30;29(2):118-124. doi: 10.3746/pnf.2024.29.2.118. Prev Nutr Food Sci. 2024. PMID: 38974586 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of advanced glycation end products on vascular smooth muscle cells under diabetic atherosclerosis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Aug 31;13:983723. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.983723. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36120471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Accelerated calciprotein crystallization time (T50) is correlated with impaired lung diffusion capacity in systemic sclerosis.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 27;15:1425885. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1425885. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39399492 Free PMC article.
-
Fisetin ameliorates vascular smooth muscle cell calcification via DUSP1-dependent p38 MAPK inhibition.Aging (Albany NY). 2025 Apr 2;17(4):885-907. doi: 10.18632/aging.206233. Epub 2025 Apr 2. Aging (Albany NY). 2025. PMID: 40179317 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of GPR39 restores defects in endothelial cell-mediated neovascularization under the duress of chronic hyperglycemia: Evidence for regulatory roles of the sonic hedgehog signaling axis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Jan 3;120(1):e2208541120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2208541120. Epub 2022 Dec 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 36574661 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of metal ion binding biomolecules one molecule at a time.Front Chem. 2024 Apr 12;12:1378447. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2024.1378447. eCollection 2024. Front Chem. 2024. PMID: 38680456 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

