Italian Children Exposure to Bisphenol A: Biomonitoring Data from the LIFE PERSUADED Project
- PMID: 34831602
- PMCID: PMC8621164
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph182211846
Italian Children Exposure to Bisphenol A: Biomonitoring Data from the LIFE PERSUADED Project
Abstract
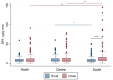
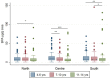
A human biomonitoring (HBM) study on bisphenol A (BPA) in Italian children and adolescents was performed within the LIFE PERSUADED project, considering the residing areas, sex and age. The median urinary BPA level was 7.02 µg/L, with children living in the South of Italy or in urban areas having higher levels than those residing in the North or in rural areas. Children aged 4-6 years had higher BPA levels than those aged 7-10 and 11-14 years, but no differences were detected between sexes. The exposure in Italian children was higher compared to children from other countries, but lower than the HBM guidance value (135 µg/L). The estimated daily intake was 0.17 μg/kg body weight (bw) per day, about 24-fold below the temporary Tolerable Daily Intake of 4 μg/kg bw per day established by the European Food Safety Authority. However, this threshold was exceeded in 1.44% of the enrolled children, raising concern about the overall exposure of Italian young population.
Keywords: Bisphenol A; age; children exposure; endocrine disruptor; geographical areas; human biomonitoring.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bolognesi C., Castle L., Cravedi J.P., Engel K.H., Fowler P.A.F., Franz R., Grob K., Gürtler R., Husøy T., Mennes W., et al. EFSA CEF Panel. Scientific Opinion on the Risks to Public Health Related to the Presence of Bisphenol A (BPA) in Foodstuffs: Executive Summary. EFSA J. 2015;13:3978. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2015.3978. - DOI
-
- Berger K., Eskenazi B., Kogut K., Parra K., Lustig R.H., Greenspan L.C., Holland N., Calafat A.M., Ye X., Harley K.G. Association of Prenatal Urinary Concentrations of Phthalates and Bisphenol A and Pubertal Timing in Boys and Girls. Environ. Health Perspect. 2018;126:097004. doi: 10.1289/EHP3424. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

