Patient-Reported Questionnaires to Identify Adverse Drug Reactions: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 34831635
- PMCID: PMC8624083
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph182211877
Patient-Reported Questionnaires to Identify Adverse Drug Reactions: A Systematic Review
Erratum in
-
Correction: Lim et al. Patient-Reported Questionnaires to Identify Adverse Drug Reactions: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 11877.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Sep 7;19(18):11209. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191811209. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36142115 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: This systematic review aims to summarise available patient-reported questionnaires to detect adverse drug reactions (ADRs) that can be utilised by healthcare professionals in clinical practice and to summarise the psychometric properties (validity, reliability, and responsiveness) of the questionnaires.
Methods: A systematic literature search was conducted using Medline, Pubmed, Embase, and Emcare databases to screen for articles published between January 2000 and July 2020. Data items regarding validity, reliability, and responsiveness were extracted independently by two authors. The methodological quality was assessed using the COSMIN (Consensus-Based Standards for the Selection of Health Measurement Instruments) checklist.
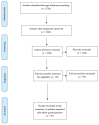
Results: A total of 1563 unique article titles were identified after removing duplicates. Following shortlisting of relevant articles, 19 patient-reported ADR questionnaires were identified. Questionnaires most commonly focused on mental health medications (42.1%, n = 8), followed by general questionnaires applicable to any medication (21.1%, n = 4). Many questionnaires did not report assessing the validity and reliability of the measurement tool. For example, only 11 questionnaires (58%) mentioned assessing content validity, in addition to criterion or construct testing.
Conclusion: This systematic review summarised the available patient-reported questionnaires that can be used in research and clinical practice to identify ADRs. Results of this systematic review highlight the need for more robust validity and reliability testing when developing patient-reported ADR questionnaires.
Keywords: adverse drug reactions; adverse events; medication safety; patient safety; questionnaire; side-effects; validity and reliability.
Conflict of interest statement
R.L. is supported by an NHMRC Early Career Fellowship. Funding received from NHMRC as part of the fellowship was used to pay for the article processing charges. All other authors declare no conflicts of interest relevant to the content of this study.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . Medication without Harm: WHO Global Patient Safety Challenge. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2017.
-
- Pharmaceutical Society of Australia . Medicine Safety: Take Care. Pharmaceutical Society of Australia; Canberra, Australia: 2019.
-
- Pharmacy Programs Administrator. Home Medicines Review. 2018. [(accessed on 30 August 2021)]. Available online: https://www.ppaonline.com.au/programs/medication-management-programs/hom....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials