Spatial Clustering of County-Level COVID-19 Rates in the U.S
- PMID: 34831926
- PMCID: PMC8622138
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph182212170
Spatial Clustering of County-Level COVID-19 Rates in the U.S
Abstract
Despite the widespread prevalence of cases associated with the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, little is known about the spatial clustering of COVID-19 in the United States. Data on COVID-19 cases were used to identify U.S. counties that have both high and low COVID-19 incident proportions and clusters. Our results suggest that there are a variety of sociodemographic variables that are associated with the severity of COVID-19 county-level incident proportions. As the pandemic evolved, communities of color were disproportionately impacted. Subsequently, it shifted from communities of color and metropolitan areas to rural areas in the U.S. Our final period showed limited differences in county characteristics, suggesting that COVID-19 infections were more widespread. The findings might address the systemic barriers and health disparities that may result in high incident proportions of COVID-19 clusters.
Keywords: COVID-19; applied spatial statistics; geographic information systems.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
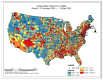
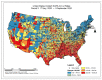
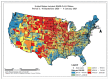
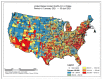
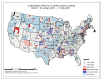
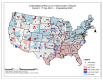
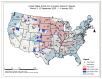

References
-
- World Health Organization Rolling Updates on Coronavirus Disease (SARS-CoV-2) 2020. [(accessed on 26 June 2020)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/events-a....
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

