Short-Term Effect of Induced Alterations in Testosterone Levels on Fasting Plasma Amino Acid Levels in Healthy Young Men
- PMID: 34833152
- PMCID: PMC8619397
- DOI: 10.3390/life11111276
Short-Term Effect of Induced Alterations in Testosterone Levels on Fasting Plasma Amino Acid Levels in Healthy Young Men
Abstract
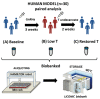
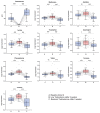
Long term effect of testosterone (T) deficiency impairs metabolism and is associated with muscle degradation and metabolic disease. The association seems to have a bidirectional nature and is not well understood. The present study aims to investigate the early and unidirectional metabolic effect of induced T changes by measuring fasting amino acid (AA) levels in a human model, in which short-term T alterations were induced. We designed a human model of 30 healthy young males with pharmacologically induced T changes, which resulted in three time points for blood collection: (A) baseline, (B) low T (3 weeks post administration of gonadotropin releasing hormone antagonist) and (C) restored T (2 weeks after injection of T undecanoate). The influence of T on AAs was analyzed by spectrophotometry on plasma samples. Levels of 9 out of 23 AAs, of which 7 were essential AAs, were significantly increased at low T and are restored upon T supplementation. Levels of tyrosine and phenylalanine were most strongly associated to T changes. Short-term effect of T changes suggests an increased protein breakdown that is restored upon T supplementation. Fasting AA levels are able to monitor the early metabolic changes induced by the T fluctuations.
Keywords: gluconeogenesis; protein breakdown; testosterone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Protein and Amino Acids—Recommended Dietary Allowances—NCBI Bookshelf. [(accessed on 24 September 2021)]; Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK234922/
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

