Rosai-Dorfman Disease: Breast Involvement-Case Report and Literature Review
- PMID: 34833385
- PMCID: PMC8624438
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina57111167
Rosai-Dorfman Disease: Breast Involvement-Case Report and Literature Review
Abstract
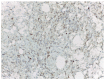
Background and objectives: Rosai-Dorfman disease (RDD) is a type of histiocytosis that usually appears in young adults or children as bilateral cervical lymphadenopathy, but extranodal involvement in not uncommon. Although the pathogenesis is not entirely elucidated, recent studies showed a possible neoplastic process. Materials and methods: Our manuscript presents a rare case of Rosai-Dorfman disease of the breast, the management of this rare case, and a literature review. There are few cases reported of RDD of the breast (around 90 globally reported cases); the data is poor, and the management not yet standardized for these cases. The case reported here shows the importance of correct breast investigation, breast imaging, and ultrasound-guided biopsy that provided an accurate diagnosis and guided further management. Results: Although RDD of the breast was rarely presented as bilateral disease in other case reports, our case showed bilateral breast disease with the suspicion of breast cancer on imaging. Pathology and immunohistochemistry were of critical importance and showed a specific pattern for histiocytosis. A multidisciplinary approach was taken into consideration for these cases in order to establish the approach. Some patients underwent surgery, but watchful waiting and close follow-up were the preferred approach. Conclusions: RDD of the breast is a rare form of histiocytosis, with fewer than 100 globally published cases. Although the management of this disease is not established yet by guidelines, a follow-up approach should be enough for these patients, and surgery might be overtreatment. Mortality from RDD is very low due to comorbidities. A multidisciplinary team decision is important, and abstinence might significantly benefit these patients.
Keywords: Rosai–Dorfman disease; Rosai–Dorfman of breast; breast pathology; histiocytosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Destombes P. Adenitis with lipid excess, in children or young adults, seen in the Antilles and in Mali (4 cases) Bull. Soc. Pathol. Exot. 1965;58:1169–1175. - PubMed
-
- Rosai J., Dorfman R.F. Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy. A newly recognized benign clinicopathological entity. Arch. Pathol. 1969;87:63–70. - PubMed
-
- Symss N., Cugati G., Vasudevan M., Ramamurthi R., Pande A. Intracranial Rosai Dorfman Disease: Report of three cases and literature review. [(accessed on 6 April 2015)];Asian J. Neurosurg. 2010 5:19–30. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3201083/ - PMC - PubMed
-
- Emile J.F., Abla O., Fraitag S., Horne A., Haroche J., Donadieu J., Requena-Caballero L., Jordan M.B., Abdel-Wahab O., Allen C.E., et al. Histiocyte Society. Revised classification of histiocytoses and neoplasms of the macrophage-dendritic cell lineages. Blood. 2016;127:2672–2681. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-01-690636. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

