Predicting the Cochlear Dead Regions Using a Machine Learning-Based Approach with Oversampling Techniques
- PMID: 34833410
- PMCID: PMC8625869
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina57111192
Predicting the Cochlear Dead Regions Using a Machine Learning-Based Approach with Oversampling Techniques
Abstract
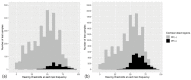
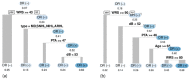
Background and Objectives: Determining the presence or absence of cochlear dead regions (DRs) is essential in clinical practice. This study proposes a machine learning (ML)-based model that applies oversampling techniques for predicting DRs in patients. Materials and Methods: We used recursive partitioning and regression for classification tree (CT) and logistic regression (LR) as prediction models. To overcome the imbalanced nature of the dataset, oversampling techniques to duplicate examples in the minority class or to synthesize new examples from existing examples in the minority class were adopted, namely the synthetic minority oversampling technique (SMOTE). Results: The accuracy results of the 10-fold cross-validation of the LR and CT with the original data were 0.82 (±0.02) and 0.93 (±0.01), respectively. The accuracy results of the 10-fold cross-validation of the LR and CT with the oversampled data were 0.66 (±0.02) and 0.86 (±0.01), respectively. Conclusions: This study is the first to adopt the SMOTE method to assess the role of oversampling methods on audiological datasets and to develop an ML-based model. Considering that the SMOTE method did not improve the model's performance, a more flexible model or more clinical features may be needed.
Keywords: cochlear dead region; machine learning; oversampling method; prediction model; synthetic minority oversampling technique.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Improving Surgical Site Infection Prediction Using Machine Learning: Addressing Challenges of Highly Imbalanced Data.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Feb 19;15(4):501. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15040501. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40002652 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Oversampling with SMOTE on the Performance of 3 Classifiers in Prediction of Type 2 Diabetes.Med Decis Making. 2016 Jan;36(1):137-44. doi: 10.1177/0272989X14560647. Epub 2014 Dec 1. Med Decis Making. 2016. PMID: 25449060
-
Enhancing and improving the performance of imbalanced class data using novel GBO and SSG: A comparative analysis.Neural Netw. 2024 May;173:106157. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2024.106157. Epub 2024 Feb 2. Neural Netw. 2024. PMID: 38335796
-
A comprehensive data level analysis for cancer diagnosis on imbalanced data.J Biomed Inform. 2019 Feb;90:103089. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2018.12.003. Epub 2019 Jan 3. J Biomed Inform. 2019. PMID: 30611011 Review.
-
Hybrid feature selection and classification technique for early prediction and severity of diabetes type 2.PLoS One. 2024 Jan 18;19(1):e0292100. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0292100. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38236900 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Endovascular management of haemorrhage and vascular lesions in patients with multiple and/or severe injuries: a systematic review and clinical practice guideline update.Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2025 Jan 16;51(1):22. doi: 10.1007/s00068-024-02719-0. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2025. PMID: 39820621 Free PMC article.
-
An Integrated Machine Learning Scheme for Predicting Mammographic Anomalies in High-Risk Individuals Using Questionnaire-Based Predictors.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Aug 8;19(15):9756. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19159756. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35955112 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

