Use of Plantar Pressure Sensors to Take Weight-Bearing Foot Casts
- PMID: 34833552
- PMCID: PMC8618002
- DOI: 10.3390/s21227476
Use of Plantar Pressure Sensors to Take Weight-Bearing Foot Casts
Abstract
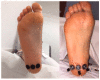
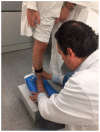
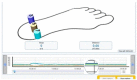
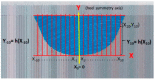
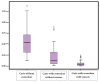
Techniques of taking casts mainly rely not on the objectivity of the procedure, but on the experience and skill of the technician. The aim of this study was to demonstrate the efficiency of a technique of taking standing foot casts controlled via pressure sensors. In this way, we mean to objectivize the degree of correction. The study was carried out through 150 procedures on 50 feet of 29 patients. The value of the "Heel Symmetry Index" was calculated on three casts in three different situations of the same foot: A first cast in which the subject did not control the position of his/her foot; a second cast where manipulations corrected the foot's pronator position; and a third cast with pressure sensors placed in the subject's heel. This enabled the control and quantification of the pressure during the manipulation when taking the cast. The comparison of the "Heel Symmetry Index" in the different groups showed significant p-values of 0.05. Conclusion: The technique of taking casts controlled by pressure sensors achieved more equilibrated casts with a better symmetry index of the heel's outline.
Keywords: foot cast; foot mold; foot orthosis; heel symmetry; insole.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Michaud T.C. Foot Orthoses and Other Form of Conservative Foot Care. Williams and Wilkins; Baltimore, MA, USA: 1993.
-
- Root M., Orien W., Weed J. Normal and Abnormal Function of the Foot. Clinical Biomechanics Corporation; Los Angeles, CA, USA: 1997.
-
- Andreasen J., Mølgaard C.M., Christensen M., Kaalund S., Lundbye-Christensen S., Simonsen O., Voigt M. Exercise therapy and custom-made insoles are effective in patients with excessive pronation and chronic foot pain—A randomized controlled trial. Foot. 2013;23:22–28. doi: 10.1016/j.foot.2012.12.001. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Reina-Bueno M., Vázquez-Bautista M.d.C., Pérez-García S., Rosende-Bautista C., Sáez-Díaz A., Munuera-Martínez P.V. Effectiveness of custom-made foot orthoses in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A randomized controlled trial. Clin. Rehabil. 2019;33:661–669. doi: 10.1177/0269215518819118. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

