Ionization of Volatile Organics and Nonvolatile Biomolecules Directly from a Titanium Slab for Mass Spectrometric Analysis
- PMID: 34833852
- PMCID: PMC8623480
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26226760
Ionization of Volatile Organics and Nonvolatile Biomolecules Directly from a Titanium Slab for Mass Spectrometric Analysis
Abstract
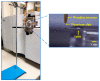
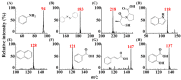
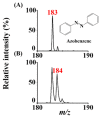
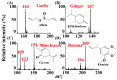
Atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (APCI)-mass spectrometry (MS) and electrospray ionization (ESI)-MS can cover the analysis of analytes from low to high polarities. Thus, an ion source that possesses these two ionization functions is useful. Atmospheric surface-assisted ionization (ASAI), which can be used to ionize polar and nonpolar analytes in vapor, liquid, and solid forms, was demonstrated in this study. The ionization of analytes through APCI or ESI was induced from the surface of a metal substrate such as a titanium slab. ASAI is a contactless approach operated at atmospheric pressure. No electric contacts nor any voltages were required to be applied on the metal substrate during ionization. When placing samples with high vapor pressure in condensed phase underneath a titanium slab close to the inlet of the mass spectrometer, analytes can be readily ionized and detected by the mass spectrometer. Furthermore, a sample droplet (~2 μL) containing high-polarity analytes, including polar organics and biomolecules, was ionized using the titanium slab. One titanium slab is sufficient to induce the ionization of analytes occurring in front of a mass spectrometer applied with a high voltage. Moreover, this ionization method can be used to detect high volatile or polar analytes through APCI-like or ESI-like processes, respectively.
Keywords: APCI; ESI; ambient ionization; nonpolar; titanium; volatile.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Carroll D.I., Dzidic I., Stillwell R.N., Haegele K.D., Horning E.C. Atmospheric pressure ionization mass spectrometry. Corona discharge ion source for use in a liquid chromatograph-mass spectrometer-computer analytical system. Anal. Chem. 1975;47:2369–2373. doi: 10.1021/ac60364a031. - DOI
-
- Yamashita M., Fenn J.B. Electrospray ion source. Another variation on the free-jet theme. J. Phys. Chem. 1984;88:4451–4459. doi: 10.1021/j150664a002. - DOI
-
- Kebarle P., Tang L. From ions in solution to ions in the gas phase-the mechanism of electrospray mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 1993;65:972A–986A. doi: 10.1021/ac00070a001. - DOI
-
- Peschke M., Verkerk U.H., Kebarle P. Features of the ESI mechanism that affect the observation of multiply charged noncovalent protein complexes and the determination of the association constant by the titration method. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2004;15:1424–1434. doi: 10.1016/j.jasms.2004.05.005. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

