1H-NMR Metabolomics as a Tool for Winemaking Monitoring
- PMID: 34833863
- PMCID: PMC8621607
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26226771
1H-NMR Metabolomics as a Tool for Winemaking Monitoring
Abstract
The chemical composition of wine is known to be influenced by multiple factors including some viticulture practices and winemaking processes. 1H-NMR metabolomics has been successfully applied to the study of wine authenticity. In the present study, 1H-NMR metabolomics in combination with multivariate analysis was applied to investigate the effects of grape maturity and enzyme and fining treatments on Cabernet Sauvignon wines. A total of forty wine metabolites were quantified. Three different stages of maturity were studied (under-maturity, maturity and over-maturity). Enzyme treatments were carried out using two pectolytic enzymes (E1 and E2). Finally, two proteinaceous fining treatments were compared (vegetable protein, fining F1; pea protein and PVPP, fining F2). The results show a clear difference between the three stages of maturity, with an impact on different classes of metabolites including amino acids, organic acids, sugars, phenolic compounds, alcohols and esters. A clear separation between enzymes E1 and E2 was observed. Both fining agents had a significant effect on metabolite concentrations. The results demonstrate that 1H-NMR metabolomics provides a fast and robust approach to study the effect of winemaking processes on wine metabolites. These results support the interest to pursue the development of 1H-NMR metabolomics to investigate the effects of winemaking on wine quality.
Keywords: 1H-NMR; metabolomics; wine; winemaking.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
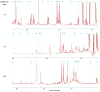
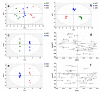
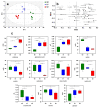
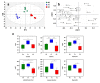
References
-
- Cevallos-Cevallos J.M., Reyes-De-Corcuera J.I., Etxeberria E., Danyluk M.D., Rodrick G.E. Metabolomic analysis in food science: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2009;20:557–566. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2009.07.002. - DOI
-
- Valls Fonayet J., Loupit G., Richard T. Chapter Ten—MS- and NMR-metabolomic tools for the discrimination of wines: Applications for authenticity. Adv. Bot. Res. 2021;98:297–357.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

