Soluble Dietary Fiber, One of the Most Important Nutrients for the Gut Microbiota
- PMID: 34833893
- PMCID: PMC8624670
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26226802
Soluble Dietary Fiber, One of the Most Important Nutrients for the Gut Microbiota
Abstract
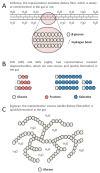
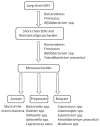
Dietary fiber is a widely recognized nutrient for human health. Previous studies proved that dietary fiber has significant implications for gastrointestinal health by regulating the gut microbiota. Moreover, mechanistic research showed that the physiological functions of different dietary fibers depend to a great extent on their physicochemical characteristics, one of which is solubility. Compared with insoluble dietary fiber, soluble dietary fiber can be easily accessed and metabolized by fiber-degrading microorganisms in the intestine and produce a series of beneficial and functional metabolites. In this review, we outlined the structures, characteristics, and physiological functions of soluble dietary fibers as important nutrients. We particularly focused on the effects of soluble dietary fiber on human health via regulating the gut microbiota and reviewed their effects on dietary and clinical interventions.
Keywords: gut microbiota; human health; resistant oligosaccharide; soluble dietary fiber; viscous fiber.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Strate L.L., Keeley B.R., Cao Y., Wu K., Giovannucci E.L., Chan A.T. Western Dietary Pattern Increases, and Prudent Dietary Pattern Decreases, Risk of Incident Diverticulitis in a Prospective Cohort Study. Gastroenterology. 2017;152:1023–1030.e2. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.12.038. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

