Microbial Efflux Pump Inhibitors: A Journey around Quinoline and Indole Derivatives
- PMID: 34834098
- PMCID: PMC8618814
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26226996
Microbial Efflux Pump Inhibitors: A Journey around Quinoline and Indole Derivatives
Abstract
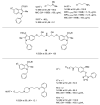
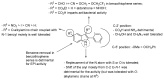
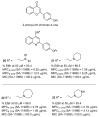
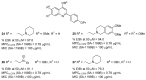
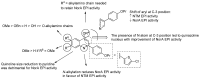
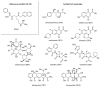
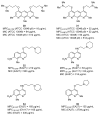
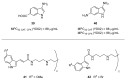
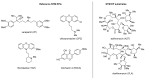
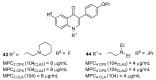
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a complex threat to human health and, to date, it represents a hot topic in drug discovery. The use of non-antibiotic molecules to block resistance mechanisms is a powerful alternative to the identification of new antibiotics. Bacterial efflux pumps exert the early step of AMR development, allowing the bacteria to grow in presence of sub-inhibitory drug concentration and develop more specific resistance mechanisms. Thus, efflux pump inhibitors (EPIs) offer a great opportunity to fight AMR, potentially restoring antibiotic activity. Based on our experience in designing and synthesizing novel EPIs, herein, we retrieved information around quinoline and indole derivatives reported in literature on this topic. Thus, our aim was to collect all data around these promising classes of EPIs in order to delineate a comprehensive structure-activity relationship (SAR) around each core for different microbes. With this review article, we aim to help future research in the field in the discovery of new microbial EPIs with improved activity and a better safety profile.
Keywords: antibiotic resistance; antibiotic resistance breakers; antimicrobial resistance; efflux pump inhibitors; microbial efflux pumps.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
2-Phenylquinoline S. aureus NorA Efflux Pump Inhibitors: Evaluation of the Importance of Methoxy Group Introduction.J Med Chem. 2018 Sep 13;61(17):7827-7848. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b00791. Epub 2018 Aug 17. J Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 30067360
-
From Quinoline to Quinazoline-Based S. aureus NorA Efflux Pump Inhibitors by Coupling a Focused Scaffold Hopping Approach and a Pharmacophore Search.ChemMedChem. 2021 Oct 6;16(19):3044-3059. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.202100282. Epub 2021 Jun 26. ChemMedChem. 2021. PMID: 34032014 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotic Potentiation Through Phytochemical-Based Efflux Pump Inhibitors to Combat Multidrug Resistance Bacteria.Med Chem. 2024;20(6):557-575. doi: 10.2174/0115734064263586231022135644. Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 37907487 Review.
-
C-2 phenyl replacements to obtain potent quinoline-based Staphylococcus aureus NorA inhibitors.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2020 Dec;35(1):584-597. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2020.1719083. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31992093 Free PMC article.
-
Current Advances in Developing Inhibitors of Bacterial Multidrug Efflux Pumps.Curr Med Chem. 2016;23(10):1062-81. doi: 10.2174/0929867323666160304150522. Curr Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 26947776 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prenylated isoflavonoids from Fabaceae against the NorA efflux pump in Staphylococcus aureus.Sci Rep. 2023 Dec 18;13(1):22548. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-48992-8. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38110428 Free PMC article.
-
Efflux, Signaling and Warfare in a Polymicrobial World.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Apr 8;12(4):731. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12040731. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37107093 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Vitro and In Vivo Investigations into the Potential of Quinazoline and Quinoline Derivatives as NorA Efflux Pump Inhibitors Against Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Strains.Antibiotics (Basel). 2025 Mar 26;14(4):339. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics14040339. Antibiotics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40298471 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic and Semisynthetic Compounds as Antibacterials Targeting Virulence Traits in Resistant Strains: A Narrative Updated Review.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 May 25;12(6):963. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12060963. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37370282 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antimicrobial Strategies Proposed for the Treatment of S. pseudintermedius and Other Dermato-Pathogenic Staphylococcus spp. in Companion Animals: A Narrative Review.Vet Sci. 2024 Jul 11;11(7):311. doi: 10.3390/vetsci11070311. Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 39057995 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization . Global Antimicrobial Resistance and Use Surveillance System (GLASS) Report: 2021. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2021.
-
- Kyriakides S. EU Action on Antimicrobial Resistance|Public Health. 2016. [(accessed on 16 November 2021)]. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/health/antimicrobial-resistance/eu-action-on-antimi....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

