Andrographolide: A Herbal-Chemosynthetic Approach for Enhancing Immunity, Combating Viral Infections, and Its Implication on Human Health
- PMID: 34834128
- PMCID: PMC8622020
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26227036
Andrographolide: A Herbal-Chemosynthetic Approach for Enhancing Immunity, Combating Viral Infections, and Its Implication on Human Health
Abstract
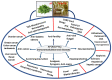
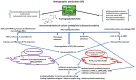
Plants consistently synthesize and accumulate medically valuable secondary metabolites which can be isolated and clinically tested under in vitro conditions. An advancement with such important phytochemical production has been recognized and utilized as herbal drugs. Bioactive andrographolide (AGL; C20H30O5) isolated from Andrographis paniculate (AP) (Kalmegh) is a diterpenoid lactones having multifunctional medicinal properties including anti-manic, anti-inflammatory, liver, and lung protective. AGL is known for its immunostimulant activity against a variety of microbial infections thereby, regulating classical and alternative macrophage activation, Ag-specific antibody production during immune disorder therapy. In vitro studies with AGL found it to be effective against multiple tumors, neuronal disorders, diabetes, pneumonia, fibrosis, and other diverse therapeutic misadventures. Generally, virus-based diseases like ZIKA, influenza A virus subtype (H1NI), Ebola (EBOV), Dengue (DENV), and coronavirus (COVID-19) epidemics have greatly increased scientific interest and demands to develop more effective and economical immunomodulating drugs with minimal side effects. Trials and in vitro pharmacological studies with AGL and medicinally beneficial herbs might contribute to benefit the human population without using chemical-based synthetic drugs. In this review, we have discussed the possible role of AGL as a promising herbal-chemo remedy during human diseases, viral infections and as an immunity booster.
Keywords: Andrographis paniculata (AP); COVID-19 epidemic; andrographolide (AGL); anti-manic; anti-microbial; herbal-chemo remedy; immune booster.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Okhuarobo A., Ehizogie Falodun J., Erharuyi O., Imieje V., Falodun A., Langer P. Harnessing the medicinal properties of andrographis paniculata for diseases and beyond: A review of its phytochemistry and pharmacology. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Dis. 2014;4:213–222. doi: 10.1016/S2222-1808(14)60509-0. - DOI
-
- Sinha R.K., Sharma S.N., Verma S.S., Zha J. Effects of lovastin, fosmidomycin and methyl jasmonate on andrographolide biosynthesis in the andrographis paniculata. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2018;40:1–11.
-
- Shaik H.A., Mishra A., Sehnal F. Silk recycling in larvae of the wax moth, galleria mellonella (lepidoptera: Pyralidae) Eur. J. Entomol. 2017;114:61–65. doi: 10.14411/eje.2017.009. - DOI
-
- Shaik H.A., Mishra A., Hussein H.M., Skoková Habuštová O., Sehnal F. Competitive interactions between entomopathogenic nematodes and parasitoid venom. J. Appl. Entomol. 2020;144:481–490. doi: 10.1111/jen.12750. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

