Selective CNS Targeting and Distribution with a Refined Region-Specific Intranasal Delivery Technique via the Olfactory Mucosa
- PMID: 34834319
- PMCID: PMC8620656
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13111904
Selective CNS Targeting and Distribution with a Refined Region-Specific Intranasal Delivery Technique via the Olfactory Mucosa
Abstract
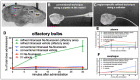
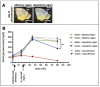
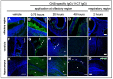
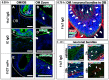
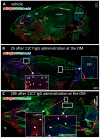
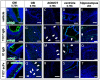
Intranasal drug delivery is a promising approach for the delivery of drugs to the CNS, but too heterogenous, unprecise delivery methods without standardization decrease the quality of many studies in rodents. Thus, the lack of a precise and region-specific application technique for mice is a major drawback. In this study, a previously developed catheter-based refined technique was validated against the conventional pipette-based method and used to specifically reach the olfactory or the respiratory nasal regions. This study successfully demonstrated region-specific administration at the olfactory mucosa resulting in over 20% of the administered fluorescein dose in the olfactory bulbs, and no peripheral bioactivity of insulin detemir and Fc-dependent uptake of two murine IgG1 (11C7 and P3X) along the olfactory pathway to cortex and hippocampus. An scFv of 11C7 showed hardly any uptake to the CNS. Elimination was dependent on the presence of the IgG's antigen. In summary, it was successfully demonstrated that region-specific intranasal administration via the olfactory region resulted in improved brain targeting and reduced peripheral targeting in mice. The data are discussed with regard to their clinical potential.
Keywords: CNS drug delivery; CNS targeting; biopharmaceuticals; nose to brain drug delivery; refined drug delivery; therapeutic antibodies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intranasal Nose-to-Brain Drug Delivery via the Olfactory Region in Mice: Two In-Depth Protocols for Region-Specific Intranasal Application of Antibodies and for Expression Analysis of Fc Receptors via In Situ Hybridization in the Nasal Mucosa.Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2754:387-410. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3629-9_21. Methods Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38512678
-
Intranasal delivery of insulin via the olfactory nerve pathway.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2012 Dec;64(12):1709-14. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.2012.01555.x. Epub 2012 Jul 4. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 23146033
-
Establishment of an Olfactory Region-specific Intranasal Delivery Technique in Mice to Target the Central Nervous System.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jan 10;12:789780. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.789780. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35082672 Free PMC article.
-
Tailoring Formulations for Intranasal Nose-to-Brain Delivery: A Review on Architecture, Physico-Chemical Characteristics and Mucociliary Clearance of the Nasal Olfactory Mucosa.Pharmaceutics. 2018 Aug 3;10(3):116. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics10030116. Pharmaceutics. 2018. PMID: 30081536 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent patents review on intranasal administration for CNS drug delivery.Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2008;2(1):25-40. doi: 10.2174/187221108783331429. Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2008. PMID: 19075895 Review.
Cited by
-
Insulin Delivery to the Brain via the Nasal Route: Unraveling the Potential for Alzheimer's Disease Therapy.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2024 Jul;14(7):1776-1793. doi: 10.1007/s13346-024-01558-1. Epub 2024 Mar 5. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 38441832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Vivo Evaluation of Nose-to-Brain Delivery of Liposomal Donepezil, Memantine, and BACE-1 siRNA for Alzheimer's Disease Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 26;25(19):10357. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910357. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408684 Free PMC article.
-
Significantly Increased Aqueous Solubility of Piperine via Nanoparticle Formulation Serves as the Most Critical Factor for Its Brain Uptake Enhancement.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Mar 30;20:3945-3959. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S506827. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40181831 Free PMC article.
-
The Nasal-Brain Drug Delivery Route: Mechanisms and Applications to Central Nervous System Diseases.MedComm (2020). 2025 Jun 6;6(6):e70213. doi: 10.1002/mco2.70213. eCollection 2025 Jun. MedComm (2020). 2025. PMID: 40487748 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Editorial: Intranasal Drug Delivery: Challenges and Opportunities.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Mar 2;13:868986. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.868986. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35308245 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Grants and funding
- N2B-patch' Grant No. 721098/European Commission
- FcRn in N2B/Ministerium für Wissenschaft, Forschung und Kunst Baden-Württemberg
- funds and fellowship by the Ulm and Biberach joint graduate school in pharmaceutical biotechnology/Ministerium für Wissenschaft, Forschung und Kunst Baden-Württemberg
- ZEBET '3D für 3R'/Federal Institute for Risk Assessment
- ALIVE/Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

