Recombinant BCG-Prime and DNA-Boost Immunization Confers Mice with Enhanced Protection against Mycobacterium kansasii
- PMID: 34835191
- PMCID: PMC8618695
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines9111260
Recombinant BCG-Prime and DNA-Boost Immunization Confers Mice with Enhanced Protection against Mycobacterium kansasii
Abstract
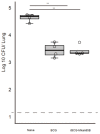
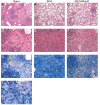
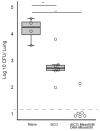
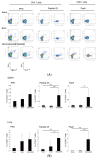
The incidence of infections with nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) has been increasing worldwide. The emergence of multidrug-resistant NTM is a serious clinical concern, and a vaccine for NTM has not yet been developed. We previously developed a new recombinant Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (rBCG) vaccine encoding the antigen 85B (Ag85B) protein of Mycobacterium kansasii-termed rBCG-Mkan85B-which was used together with a booster immunization with plasmid DNA expressing the same M. kansasii Ag85B gene (DNA-Mkan85B). We reported that rBCG-Mkan85B/DNA-Mkan85B prime-boost immunization elicited various NTM strain-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cells and induced Mycobacterium tuberculosis-specific immunity. In this study, to investigate the protective effect against M. kansasii infection, we challenged mice vaccinated with a rBCG-Mkan85B or rBCG-Mkan85B/DNA-Mkan85B prime-boost strategy with virulent M. kansasii. Although BCG and rBCG-Mkan85B immunization each suppressed the growth of M. kansasii in the mouse lungs, the rBCG-Mkan85B/DNA-Mkan85B prime-boost vaccination reduced the bacterial burden more significantly. Moreover, the rBCG-Mkan85B/DNA-Mkan85B prime-boost vaccination induced antigen-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. Our data suggest that rBCG-Mkan85B/DNA-Mkan85B prime-boost vaccination effectively enhances antigen-specific T cells. Our novel rBCG could be a potential alternative to clinical BCG for preventing various NTM infections.
Keywords: CD4+ T Cells; CD8+ T Cells; Mycobacterium kansasii; recombinant BCG.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Induction of Antigen 85B-Specific CD8+ T Cells by Recombinant BCG Protects against Mycobacterial Infection in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 4;24(2):966. doi: 10.3390/ijms24020966. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36674484 Free PMC article.
-
MHC-restricted Ag85B-specific CD8+ T cells are enhanced by recombinant BCG prime and DNA boost immunization in mice.Eur J Immunol. 2019 Sep;49(9):1399-1414. doi: 10.1002/eji.201847988. Epub 2019 Jun 19. Eur J Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31135967 Free PMC article.
-
Prime-boost vaccination with rBCG/rAd35 enhances CD8⁺ cytolytic T-cell responses in lesions from Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected primates.Mol Med. 2012 May 9;18(1):647-58. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2011.00222. Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22396020 Free PMC article.
-
[Novel vaccines against M. tuberculosis].Kekkaku. 2006 Dec;81(12):745-51. Kekkaku. 2006. PMID: 17240920 Review. Japanese.
-
Is interferon-gamma the right marker for bacille Calmette-Guérin-induced immune protection? The missing link in our understanding of tuberculosis immunology.Clin Exp Immunol. 2012 Sep;169(3):213-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2012.04614.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22861360 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A temperature-responsive PLA-based nanosponge as a novel nanoadjuvant and efficient delivery carrier of Ag85B for effective vaccine against Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Cell Commun Signal. 2025 Apr 1;23(1):159. doi: 10.1186/s12964-025-02105-2. Cell Commun Signal. 2025. PMID: 40170045 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoinformatic design of a multivalent vaccine against Brucella abortus and its evaluation in a murine model using a DNA prime-protein boost strategy.Front Immunol. 2024 Nov 21;15:1456078. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1456078. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39640259 Free PMC article.
-
The Induction of Antigen 85B-Specific CD8+ T Cells by Recombinant BCG Protects against Mycobacterial Infection in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 4;24(2):966. doi: 10.3390/ijms24020966. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36674484 Free PMC article.
-
Advance in strategies to build efficient vaccines against tuberculosis.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Nov 24;9:955204. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.955204. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 36504851 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Maekura R., Okuda Y., Hirotani A., Kitada S., Hiraga T., Yoshimura K., Yano I., Kobayashi K., Ito M. Clinical and prognostic importance of serotyping Mycobacterium avium-Mycobacterium intracellulare complex isolates in human immunodeficiency virus-negative patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005;43:3150–3158. doi: 10.1128/JCM.43.7.3150-3158.2005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- de Mello K.G., Mello F.C., Borga L., Rolla V., Duarte R.S., Sampaio E.P., Holland S.M., Prevots D.R., Dalcolmo M.P. Clinical and therapeutic features of pulmonary nontuberculous mycobacterial disease, Brazil, 1993–2011. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013;19:393–399. doi: 10.3201/eid/1903.120735. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

