Anti-Spike SARS-CoV-2 IgG Assessment with a Commercial Assay during a 4-Month Course after COVID-19 Vaccination
- PMID: 34835298
- PMCID: PMC8617658
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines9111367
Anti-Spike SARS-CoV-2 IgG Assessment with a Commercial Assay during a 4-Month Course after COVID-19 Vaccination
Abstract
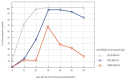
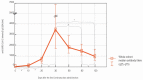
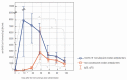
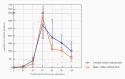
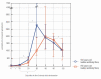
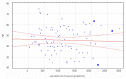
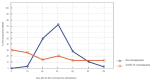
We intended to assess the humoral response induced by the Pfizer/BioNTech Comirnaty COVID-19 vaccine with commercially available immunoassays: anti-spike (S) IgG and IgM, and anti-nucleocapsid (N) IgG antibodies, over a 4-month course. One hundred subjects, including 15 COVID-19 convalescents, comprised the study cohort. The SARS-CoV-2 antibodies concentrations were measured on day 0' and 10', 20', 30', 60', 90', and 120' after the first dose administration. Over the course of the study, 100% of the participants developed and sustained anti-SARS-CoV-2 S IgG antibodies. The highest concentration, exceeding the quantification range of the test (2080 BAU/mL), was reached by 67% of the subjects on day 30'. The concentration of the antibodies remained stable between days 30' and 90' but was followed by a significant decrease between days 90' and 120'. The stronger and more persistent humoral response was noted for women. The COVID-19 convalescents developed higher antibody levels, particularly 10 days after the first Comirnaty dose. Twenty-three out of the eighty-five naïve vaccinees failed to develop a detectable IgM response. LIAISON® SARS-CoV-2 TrimericS IgG (DiaSorin S.p.A, Saluggia, Italy) may be useful in the assessment of the humoral response to the Comirnaty vaccine. In contrast, Abbott's anti-S SARS-CoV-2 IgM has a limited utility in this context.
Keywords: COVID-19 testing; COVID-19 vaccines; COVID-19 vaccines booster shot; SARS-CoV-2 antibodies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- COVID-19 Treatments: Authorised. [(accessed on 2 September 2021)]. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/human-regulatory/overview/public-health-thr....
-
- Patelarou E., Galanis P., Mechili E.A., Argyriadi A., Argyriadis A., Asimakopoulou E., Brokaj S., Bucaj J., Carmona-Torres J.M., Cobo-Cuenca A.I., et al. Factors influencing nursing students’ intention to accept COVID-19 vaccination: A pooled analysis of seven European countries. Nurse Educ. Today. 2021;104:105010. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2021.105010. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rastawicki W., Rokosz-Chudziak N. Characteristics and assessment of the usefulness of serological tests in the diagnostic of infections caused by coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 on the basis of available manufacturer’s data and literature review. Prz. Epidemiol. 2020;74:49–68. doi: 10.32394/pe.74.11. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

