Ultrasensitive Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Proteins Using the Thio-NAD Cycling Reaction: A Preliminary Study before Clinical Trials
- PMID: 34835340
- PMCID: PMC8619787
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms9112214
Ultrasensitive Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Proteins Using the Thio-NAD Cycling Reaction: A Preliminary Study before Clinical Trials
Abstract
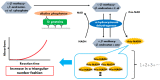
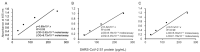
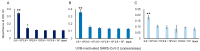
To help control the global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), we developed a diagnostic method targeting the spike protein of the virus that causes the infection, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). We applied an ultrasensitive method by combining a sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and the thio-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (thio-NAD) cycling reaction to quantify spike S1 proteins. The limit of detection (LOD) was 2.62 × 10-19 moles/assay for recombinant S1 proteins and 2.6 × 106 RNA copies/assay for ultraviolet B-inactivated viruses. We have already shown that the ultrasensitive ELISA for nucleocapsid proteins can detect ultraviolet B-inactivated viruses at the 104 RNA copies/assay level, whereas the nucleocapsid proteins of SARS-CoV-2 are difficult to distinguish from those in conventional coronaviruses and SARS-CoV. Thus, an antigen test for only the nucleocapsid proteins is insufficient for virus specificity. Therefore, the use of a combination of tests against both spike and nucleocapsid proteins is recommended to increase both the detection sensitivity and testing accuracy of the COVID-19 antigen test. Taken together, our present study, in which we incorporate S1 detection by combining the ultrasensitive ELISA for nucleocapsid proteins, offers an ultrasensitive, antigen-specific test for COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; antigen test; spike protein; thio-NAD cycling; ultrasensitive ELISA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Premkumar L., Segovia-Chumbez B., Jadi R., Martinez D.R., Raut R., Markmann A., Cornaby C., Bartelt L., Weiss S., Park Y., et al. The receptor binding domain of the viral spike protein is an immunodominant and highly specific target of antibodies in SARS-CoV-2 patients. Sci. Immunol. 2020;5:eabc8413. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abc8413. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

