Campylobacter jejuni in Different Canine Populations: Characteristics and Zoonotic Potential
- PMID: 34835357
- PMCID: PMC8618475
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms9112231
Campylobacter jejuni in Different Canine Populations: Characteristics and Zoonotic Potential
Abstract
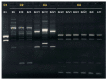
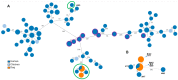
With most epidemiological studies focused on poultry, dogs are often overlooked as a reservoir of Campylobacter, even though these animals maintain close daily contact with humans. The present study aimed to obtain a first insight into the presence and characteristics of Campylobacter spp. in different canine populations in Portugal, and to evaluate its zoonotic potential through genomic analysis. From a total of 125 rectal swabs collected from companion (n = 71) and hunting dogs (n = 54) living in two different settings, rural (n = 75) and urban (n = 50), 32 Campylobacter spp. isolates were obtained. Four different Campylobacter species were identified by Multiplex PCR and MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry, of which Campylobacter jejuni (n = 14, 44%) was overall the most frequently found species. Relevant resistance phenotypes were detected in C. jejuni, with 93% of the isolates being resistant to ciprofloxacin, 64% to tetracycline, and 57% to ampicillin, and three isolates being multi-drug-resistant. Comparison of the phenotypic and genotypic traits with human isolates from Portuguese patients revealed great similarity between both groups. Particularly relevant, the wgMLST analysis allowed the identification of isolates from human and dogs without any apparent epidemiological relationship, sharing high genetic proximity. Notwithstanding the limited sample size, considering the high genomic diversity of C. jejuni, the genetic overlap between human and dog strains observed in this study confirmed that the occurrence of this species in dogs is of public health concern, reinforcing the call for a One Health approach.
Keywords: Campylobacter spp.; One Health; dogs; whole genome sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Mullner P., Spencer S.E.F., Wilson D.J., Jones G., Noble A.D., Midwinter A.C., Collins-Emerson J.M., Carter P., Hathaway S., French N.P. Assigning the source of human campylobacteriosis in New Zealand: A comparative genetic and epidemiological approach. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2009;9:1311–1319. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2009.09.003. - DOI - PubMed
-
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority) Scientific Opinion on Campylobacter in broiler meat production: Control options and performance objectives and/or targets at different stages of the food chain. EFSA J. 2011;9:2105. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2011.2105. - DOI
-
- EFSA and ECDC (European Food Safety Authority and European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control) The European Union Summary Report on Antimicrobial Resistance in zoonotic and indicator bacteria from humans, animals and food in 2018/2019. EFSA J. 2021;19 doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2021.6490. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

