Proteomic Analysis Explores Interactions between Lactiplantibacillus plantarum and Saccharomyces cerevisiae during Sourdough Fermentation
- PMID: 34835478
- PMCID: PMC8620635
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms9112353
Proteomic Analysis Explores Interactions between Lactiplantibacillus plantarum and Saccharomyces cerevisiae during Sourdough Fermentation
Abstract
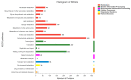
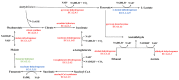
Sourdough is a fermentation culture which is formed following metabolic activities of a multiple bacterial and fungal species on raw dough. However, little is known about the mechanism of interaction among different species involved in fermentation. In this study, Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Sx3 and Saccharomyces cerevisiae Sq7 were selected. Protein changes in sourdough, fermented with single culture (either Sx3 or Sq7) and mixed culture (both Sx3 and Sq7), were evaluated by proteomics. The results show that carbohydrate metabolism in mixed-culture-based sourdough is the most important metabolic pathway. A greater abundance of L-lactate dehydrogenase and UDP-glucose 4-epimerase that contribute to the quality of sourdough were observed in mixed-culture-based sourdough than those produced by a single culture. Calreticulin, enolase, seryl-tRNA synthetase, ribosomal protein L23, ribosomal protein L16, and ribosomal protein L5 that are needed for the stability of proteins were increased in mixed-culture-based sourdough. The abundance of some compounds which play an important role in enhancing the nutritional characteristics and flavour of sourdough (citrate synthase, aldehyde dehydrogenase, pyruvate decarboxylase, pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 and acetyl-CoA) was decreased. In summary, this approach provided new insights into the interaction between L. plantarum and S. cerevisiae in sourdough, which may serve as a base for further research into the detailed mechanism.
Keywords: Lactiplantibacillus plantarum; Saccharomyces cerevisiae; amino acid metabolism; carbohydrate metabolism; proteomics; sourdough.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- De Vuyst L., Neysens P. The sourdough microflora: Biodiversity and metabolic interactions. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2005;16:43–56. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2004.02.012. - DOI
-
- Zhu J., Huang R., Hu D.X., Dou Y., Ren H.Y., Yang Z.X., Deng C., Xiong W., Wang D., Mao Y. Individualized prediction of metastatic involvement of lymph nodes posterior to the right recurrent laryngeal nerve in papillary thyroid carcinoma. OncoTargets Ther. 2019;12:9077–9084. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S220926. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

