Development of High-Throughput Multiplex Serology to Detect Serum Antibodies against Coxiella burnetii
- PMID: 34835498
- PMCID: PMC8623512
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms9112373
Development of High-Throughput Multiplex Serology to Detect Serum Antibodies against Coxiella burnetii
Abstract
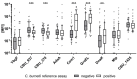
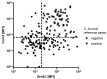
The causative agent of Q fever, the bacterium Coxiella burnetii (C. burnetii), has gained increasing interest due to outbreak events and reports about it being a potential risk factor for the development of lymphomas. In order to conduct large-scale studies for population monitoring and to investigate possible associations more closely, accurate and cost-effective high-throughput assays are highly desired. To address this need, nine C. burnetii proteins were expressed as recombinant antigens for multiplex serology. This technique enables the quantitative high-throughput detection of antibodies to multiple antigens simultaneously in a single reaction. Based on a reference group of 76 seropositive and 91 seronegative sera, three antigens were able to detect C. burnetii infections. Com1, GroEL, and DnaK achieved specificities of 93%, 69%, and 77% and sensitivities of 64%, 72%, and 47%, respectively. Double positivity to Com1 and GroEL led to a combined specificity of 90% and a sensitivity of 71%. In a subgroup of seropositives with an increased risk for chronic Q fever, the double positivity to these markers reached a specificity of 90% and a sensitivity of 86%. Multiplex serology enables the detection of antibodies against C. burnetii and appears well-suited to investigate associations between C. burnetii infections and the clinical manifestations in large-scale studies.
Keywords: Coxiella burnetii; infection marker; multiplex serology; seroepidemiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control . Technical Report: Risk Assessment on Q Fever. ECDC; Stockholm, Sweden: 2010. p. 40.
-
- Schimmer B., Notermans D.W., Harms M.G., Reimerink J.H., Bakker J., Schneeberger P., Mollema L., Teunis P., van Pelt W., van Duynhoven Y. Low seroprevalence of Q fever in The Netherlands prior to a series of large outbreaks. Epidemiol. Infect. 2012;140:27–35. doi: 10.1017/S0950268811000136. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

