Role of Maturation of Lipoproteins in the Pathogenesis of the Infection Caused by Streptococcus suis Serotype 2
- PMID: 34835511
- PMCID: PMC8621357
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms9112386
Role of Maturation of Lipoproteins in the Pathogenesis of the Infection Caused by Streptococcus suis Serotype 2
Abstract
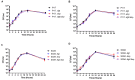
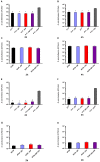
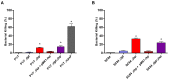
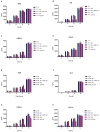
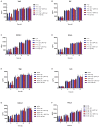
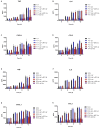
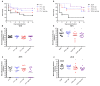
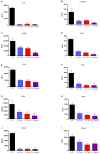
Streptococcus suis serotype 2 is an important porcine bacterial pathogen associated with multiple pathologies in piglets. Bacterial lipoproteins (LPPs) have been described as playing important roles in the pathogenesis of the infection of other Gram-positive bacteria as adhesins, pro-inflammatory cell activators and/or virulence factors. In the current study, we aimed to evaluate the role of the prolipoprotein diacylglyceryl transferase (Lgt) and lipoprotein signal peptidase (Lsp) enzymes, which are responsible for LPP maturation, on the pathogenesis of the infection caused by two different sequence types (STs) of S. suis serotype 2 strains (virulent ST1 and highly virulent ST7). Through the use of isogenic Δlgt, Δlsp and double Δlgt/Δlsp mutants, it was shown that lack of these enzymes did not influence S. suis adhesion/invasion to porcine respiratory epithelial cells. However, in the absence of the Lsp and/or Lgt, a significant reduction in the capacity of S. suis to activate phagocytic cells and induce pro-inflammatory mediators (in vitro and in vivo) was observed. In general, results obtained with the double mutant did not differ in comparison to single mutants, indicating lack of an additive effect. Finally, our data suggest that these enzymes play a differential role in virulence, depending on the genetic background of the strain and being more important for the highly virulent ST7 strain.
Keywords: Streptococcus suis; inflammation; lipoproteins; maturation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Study of the Role of Lipoprotein Maturation Enzymes in the Pathogenesis of the Infection Caused by the Streptococcus suis Serotype 2 Sequence Type 25 North American Prototype Strain.Pathogens. 2023 Nov 7;12(11):1325. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12111325. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 38003790 Free PMC article.
-
Lipoproteins are critical TLR2 activating toxins in group B streptococcal sepsis.J Immunol. 2008 May 1;180(9):6149-58. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.9.6149. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18424736
-
Structural analysis and immunostimulatory potency of lipoteichoic acids isolated from three Streptococcus suis serotype 2 strains.J Biol Chem. 2018 Aug 3;293(31):12011-12025. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.002174. Epub 2018 Jun 8. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29884769 Free PMC article.
-
Virulence factors involved in the pathogenesis of the infection caused by the swine pathogen and zoonotic agent Streptococcus suis.Future Microbiol. 2012 Feb;7(2):259-79. doi: 10.2217/fmb.11.149. Future Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22324994 Review.
-
Role of Metabolic Adaptation of Streptococcus suis to Host Niches in Bacterial Fitness and Virulence.Pathogens. 2023 Mar 31;12(4):541. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12040541. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 37111427 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Study of the Role of Lipoprotein Maturation Enzymes in the Pathogenesis of the Infection Caused by the Streptococcus suis Serotype 2 Sequence Type 25 North American Prototype Strain.Pathogens. 2023 Nov 7;12(11):1325. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12111325. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 38003790 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms Underlying the Effects of Secretory Protein G22 on Biological Characteristics and Virulence of Streptococcus suis.Microorganisms. 2025 Mar 28;13(4):774. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13040774. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40284611 Free PMC article.
-
Encapsulated Streptococcus suis impairs optimal neutrophil functions which are not rescued by priming with colony-stimulating factors.PLoS One. 2024 Jan 23;19(1):e0296844. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0296844. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38261585 Free PMC article.
-
Lipoteichoic acids influence cell shape and bacterial division of Streptococcus suis serotype 2, but play a limited role in the pathogenesis of the infection.Vet Res. 2024 Mar 19;55(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s13567-024-01287-w. Vet Res. 2024. PMID: 38504299 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hill J.E., Gottschalk M., Brousseau R., Harel J., Hemmingsen S.M., Goh S.H. Biochemical analysis, cpn60 and 16S rDNA sequence data indicate that Streptococcus suis serotypes 32 and 34, isolated from pigs, are Streptococcus orisratti. Vet. Microbiol. 2005;107:63–69. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2005.01.003. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Goyette-Desjardins G., Auger J.P., Xu J., Segura M., Gottschalk M. Streptococcus suis, an important pig pathogen and emerging zoonotic agent-an update on the worldwide distribution based on serotyping and sequence typing. Emerg. Microb. Infect. 2014;3:e45. doi: 10.1038/emi.2014.45. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

