Influence of Bioinspired Lithium-Doped Titanium Implants on Gingival Fibroblast Bioactivity and Biofilm Adhesion
- PMID: 34835563
- PMCID: PMC8618897
- DOI: 10.3390/nano11112799
Influence of Bioinspired Lithium-Doped Titanium Implants on Gingival Fibroblast Bioactivity and Biofilm Adhesion
Abstract
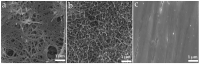
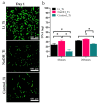
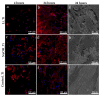
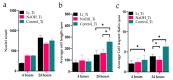
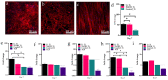
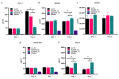
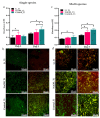
Soft tissue integration (STI) at the transmucosal level around dental implants is crucial for the long-term success of dental implants. Surface modification of titanium dental implants could be an effective way to enhance peri-implant STI. The present study aimed to investigate the effect of bioinspired lithium (Li)-doped Ti surface on the behaviour of human gingival fibroblasts (HGFs) and oral biofilm in vitro. HGFs were cultured on various Ti surfaces-Li-doped Ti (Li_Ti), NaOH_Ti and micro-rough Ti (Control_Ti)-and were evaluated for viability, adhesion, extracellular matrix protein expression and cytokine secretion. Furthermore, single species bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus) and multi-species oral biofilms from saliva were cultured on each surface and assessed for viability and metabolic activity. The results show that both Li_Ti and NaOH_Ti significantly increased the proliferation of HGFs compared to the control. Fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF-2) mRNA levels were significantly increased on Li_Ti and NaOH_Ti at day 7. Moreover, Li_Ti upregulated COL-I and fibronectin gene expression compared to the NaOH_Ti. A significant decrease in bacterial metabolic activity was detected for both the Li_Ti and NaOH_Ti surfaces. Together, these results suggest that bioinspired Li-doped Ti promotes HGF bioactivity while suppressing bacterial adhesion and growth. This is of clinical importance regarding STI improvement during the maintenance phase of the dental implant treatment.
Keywords: biofilm; gingival fibroblasts; implants; nanostructure; soft-tissue integration; surface modification; titanium.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Roos J., Sennerby L., Lekholm U.L.F., Jemt T., Gröndahl K., Albrektsson T. A qualitative and quantitative method for evaluating implant success: A 5-year retrospective analysis of the Branemark implant. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants. 1997;12:1–20. - PubMed
-
- Becker W., Becker B.E., Newman M.G., Nyman S. Clinical and microbiologic findings that may contribute to dental implant failure. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 1990;5:1–17. - PubMed
-
- Berglundh T., Armitage G., Araujo M.G., Avila-Ortiz G., Blanco J., Camargo P.M., Chen S., Cochran D., Derks J., Figuero E., et al. Peri-implant diseases and conditions: Consensus report of workgroup 4 of the 2017 world workshop on the classification of periodontal and peri-implant diseases and conditions. J. Periodontol. 2018;89:S313–S318. doi: 10.1002/JPER.17-0739. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

