Challenges and Recent Advances in Enzyme-Mediated Wastewater Remediation-A Review
- PMID: 34835887
- PMCID: PMC8625148
- DOI: 10.3390/nano11113124
Challenges and Recent Advances in Enzyme-Mediated Wastewater Remediation-A Review
Abstract
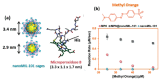
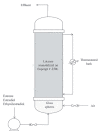
Different classes of artificial pollutants, collectively called emerging pollutants, are detected in various water bodies, including lakes, rivers, and seas. Multiple studies have shown the devastating effects these emerging pollutants can have on human and aquatic life. The main reason for these emerging pollutants in the aquatic environment is their incomplete removal in the existing wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs). Several additional treatments that could potentially supplement existing WWTPs to eliminate these pollutants include a range of physicochemical and biological methods. The use of enzymes, specifically, oxidoreductases, are increasingly being studied for their ability to degrade different classes of organic compounds. These enzymes have been immobilized on different supports to promote their adoption as a cost-effective and recyclable remediation approach. Unfortunately, some of these techniques have shown a negative effect on the enzyme, including denaturation and loss of catalytic activity. This review focuses on the major challenges facing researchers working on the immobilization of peroxidases and the recent progress that has been made in this area. It focuses on four major areas: (1) stability of enzymes upon immobilization, enzyme engineering, and evolution; (2) recyclability and reusability, including immobilization on membranes and solid supports; (3) cost associated with enzyme-based remediation; and (4) scaling-up and bioreactors.
Keywords: enzyme immobilization; hybrid nanoflowers; metal organic framework; peroxidases enzymes; water remediation enzyme evolution.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Advances in the application of immobilized enzyme for the remediation of hazardous pollutant: A review.Chemosphere. 2022 Jul;299:134390. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134390. Epub 2022 Mar 23. Chemosphere. 2022. PMID: 35339523 Review.
-
Oxidoreductases for the remediation of organic pollutants in water - a critical review.Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2018 Nov;38(7):971-988. doi: 10.1080/07388551.2017.1423275. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29385838 Review.
-
Non-magnetic and magnetically responsive support materials immobilized peroxidases for biocatalytic degradation of emerging dye pollutants-A review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2022 May 15;207:387-401. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.03.035. Epub 2022 Mar 9. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022. PMID: 35278508 Review.
-
Immobilization of Biomass Materials for Removal of Refractory Organic Pollutants from Wastewater.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Oct 24;19(21):13830. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192113830. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36360710 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Up-to-Date Review on the Remediation of Dyes and Phenolic Compounds from Wastewaters Using Enzymes Immobilized on Emerging and Nanostructured Materials: Promises and Challenges.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023 Jul 25;13(15):2152. doi: 10.3390/nano13152152. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37570470 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transforming cancer detection and treatment with nanoflowers.Med Oncol. 2024 Oct 22;41(11):295. doi: 10.1007/s12032-024-02530-2. Med Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39436526 Review.
-
Design of biomass-based renewable materials for environmental remediation.Trends Biotechnol. 2022 Dec;40(12):1519-1534. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2022.09.011. Epub 2022 Oct 27. Trends Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36374762 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Purple non-sulfur bacteria for biotechnological applications.J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Dec 31;52:kuae052. doi: 10.1093/jimb/kuae052. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39730143 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhanced Tribocatalytic Degradation of Organic Pollutants by ZnO Nanoparticles of High Crystallinity.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Dec 22;13(1):46. doi: 10.3390/nano13010046. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36615955 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmaceutical removal from wastewater by introducing cytochrome P450s into microalgae.Microb Biotechnol. 2024 Jun;17(6):e14515. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.14515. Microb Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38925623 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Petrovic M. Analysis and removal of emerging contaminants in wastewater and drinking water. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2003;22:685–696. doi: 10.1016/S0165-9936(03)01105-1. - DOI
-
- Geissen V., Mol H., Klumpp E., Umlauf G., Nadal M., van der Ploeg M., van de Zee S.E., Ritsema C.J. Emerging pollutants in the environment: A challenge for water resource management. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2015;3:57–65. doi: 10.1016/j.iswcr.2015.03.002. - DOI
-
- Farre M., Pérez S., Kantiani L., Barceló D. Fate and toxicity of emerging pollutants, their metabolites and transformation products in the aquatic environment. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2008;27:991–1007. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2008.09.010. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

