Efficacy of Creatine Supplementation Combined with Resistance Training on Muscle Strength and Muscle Mass in Older Females: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 34836013
- PMCID: PMC8619193
- DOI: 10.3390/nu13113757
Efficacy of Creatine Supplementation Combined with Resistance Training on Muscle Strength and Muscle Mass in Older Females: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
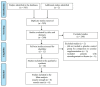
Sarcopenia refers to the age-related loss of muscle strength and muscle mass, which is associated with a reduced quality of life, particularly in older females. Resistance training (RT) is well established to be an effective intervention to counter indices of sarcopenia. Accumulating research indicates that the addition of creatine supplementation (Cr) to RT augments gains in muscle strength and muscle mass, compared to RT alone. However, some evidence indicates that sex differences may alter the effectiveness of Cr. Therefore, we systematically reviewed randomized controlled trials (RCTs) investigating the efficacy of Cr + RT on measures of upper- and lower-body strength and muscle mass in older females. A systematic literature search was performed in nine electronic databases. Ten RCTs (N = 211 participants) were included the review. Overall, Cr significantly increased measures of upper-body strength (7 studies, n = 142, p = 0.04), with no effect on lower-body strength or measures of muscle mass. Sub-analyses revealed that both upper-body (4 studies, n = 97, p = 0.05) and lower-body strength (4 studies, n = 100, p = 0.03) were increased by Cr, compared to placebo in studies ≥ 24 weeks in duration. In conclusion, older females supplementing with Cr experience significant gains in muscle strength, especially when RT lasts for at least 24 weeks in duration. However, given the level of evidence, future high-quality studies are needed to confirm these findings.
Keywords: aging; body composition; dietary supplements; ergogenic aids; exercise; sarcopenia.
Conflict of interest statement
D.G.C. has conducted industry sponsored research involving creatine supplementation, received creatine donation for scientific studies and travel support for presentations involving creatine supplementation at scientific conferences. In addition, D.G.C. serves on the Scientific Advisory Board for Alzchem (a company which manufactures creatine). S.C.F. has previously served as a Scientific Advisor for a company that sold creatine.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

