The Role of 20-HETE, COX, Thromboxane Receptors, and Blood Plasma Antioxidant Status in Vascular Relaxation of Copper-Nanoparticle-Fed WKY Rats
- PMID: 34836047
- PMCID: PMC8623823
- DOI: 10.3390/nu13113793
The Role of 20-HETE, COX, Thromboxane Receptors, and Blood Plasma Antioxidant Status in Vascular Relaxation of Copper-Nanoparticle-Fed WKY Rats
Abstract
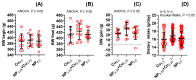
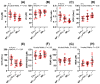
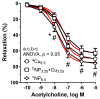
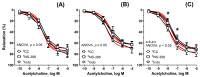
Recently, the addition of copper nanoparticles (NPs) in a daily diet (6.5 mg/kg) was studied in different animal models as a possible alternative to ionic forms. Male Wistar-Kyoto rats (24-week-old, n = 11) were fed with copper, either in the form of carbonate salt (Cu6.5) or metal-based copper NPs (NP6.5), for 8 weeks. The third group was fed with a half dose of each (NP3.25 + Cu3.25). The thoracic aorta and blood plasma was studied. Supplementation with NP6.5 decreased the Cu (×0.7), Cu/Zn-ratio (×0.6) and catalase (CAT, ×0.7), and increased Zn (×1.2) and superoxide dismutase (SOD, ×1.4). Meanwhile, NP3.25 + Cu3.25 decreased the Cu/Zn-ratio (×0.7), and CAT (×0.7), and increased the daily feed intake (×1.06). Preincubation with either the selective cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 inhibitor, or the non-selective COX-1/2 inhibitor attenuated vasodilation of rat thoracic aorta in the NP6.5 group exclusively. However, an increased vasodilator response was observed in the NP6.5 and NP3.25 + Cu3.25 group of rats after preincubation with an inhibitor of 20-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (20-HETE) formation, and the thromboxane receptor (TP) antagonist. Significant differences were observed between the NP6.5 and NP3.25 + Cu3.25 groups of rats in: dietary intake, acetylcholine-induced vasodilation, and response to COX-inhibitors. Copper NPs in a standard daily dose had more significant effects on the mechanism(s) responsible for the utilization of reactive oxygen species in the blood plasma with the participation of prostanoids derived from COX-2 in the vascular relaxation. Dietary copper NPs in both doses modified vasodilation through the vasoconstrictor 20-HETE and the TP receptors.
Keywords: 20-HETE; HET0016; NS-398; SQ-29,548; aging; furegrelate; indomethacin; thromboxane-A2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



References
-
- Majewski M., Lis B., Olas B., Ognik K., Juśkiewicz J. Dietary supplementation with copper nanoparticles influences the markers of oxidative stress and modulates vasodilation of thoracic arteries in young Wistar rats. PLoS ONE. 2020;15:e0229282. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0229282. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tang H., Xu M., Luo J., Zhao L., Ye G., Shi F., Lv C., Chen H., Wang Y., Li Y. Liver toxicity assessments in rats following sub-chronic oral exposure to copper nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2019;31:30. doi: 10.1186/s12302-019-0214-0. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

