Pathophysiology of Vascular Calcification and Bone Loss: Linked Disorders of Ageing?
- PMID: 34836090
- PMCID: PMC8623966
- DOI: 10.3390/nu13113835
Pathophysiology of Vascular Calcification and Bone Loss: Linked Disorders of Ageing?
Abstract
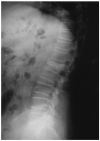
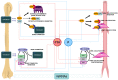
Vascular Calcification (VC), low bone mass and fragility fractures are frequently observed in ageing subjects. Although this clinical observation could be the mere coincidence of frequent age-dependent disorders, clinical and experimental data suggest that VC and bone loss could share pathophysiological mechanisms. Indeed, VC is an active process of calcium and phosphate precipitation that involves the transition of the vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) into osteoblast-like cells. Among the molecules involved in this process, parathyroid hormone (PTH) plays a key role acting through several mechanisms which includes the regulation of the RANK/RANKL/OPG system and the Wnt/ß-catenin pathway, the main pathways for bone resorption and bone formation, respectively. Furthermore, some microRNAs have been implicated as common regulators of bone metabolism, VC, left ventricle hypertrophy and myocardial fibrosis. Elucidating the common mechanisms between ageing; VC and bone loss could help to better understand the potential effects of osteoporosis drugs on the CV system.
Keywords: bone fractures; bone loss; fracture risk; mineral bone disorders; osteoporosis; vascular calcification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Garcia M.R., Diaz M.N., Cannata-Andía J.B. Bone metabolism, vascular calcifications and mortality: Associations beyond mere coincidence. J. Nephrol. 2005;18:458–463. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- GRUPIN 14-028, IDI-2018-000-152/Fondo Europeo de Desarrollo Regional (FEDER), Plan de Ciencia, Tecnología e Innovación del Principado de Asturias (2018-2022)
- RD12/0021/1023; RD16/0009/0017/Red Cooperativa en Salud REDinREN del Instituto de Salud Carlos III
- PI19/00532/Instituto de Salud Carlos III
- PI20/00633/Instituto de Salud Carlos III
- PI20/00753/Instituto de Salud Carlos III
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

