Lactic Acid Bacteria Fermented Cordyceps militaris (GRC-SC11) Suppresses IgE Mediated Mast Cell Activation and Type I Hypersensitive Allergic Murine Model
- PMID: 34836105
- PMCID: PMC8618942
- DOI: 10.3390/nu13113849
Lactic Acid Bacteria Fermented Cordyceps militaris (GRC-SC11) Suppresses IgE Mediated Mast Cell Activation and Type I Hypersensitive Allergic Murine Model
Abstract
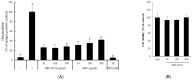
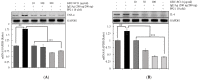
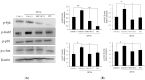
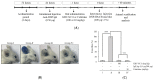
Cordyceps militaris (C. militaris) has various biomedical applications in traditional oriental medicine for different diseases including inflammatory and immune-dysregulated diseases. It is a reservoir of nutritional components such as cordycepin, polysaccharides, and antioxidants. To improve its bioactivity, we fermented C. militaris with a Pediococcus pentosaceus strain isolated from a salted small octopus (SC11). The current study aimed to evaluate whether P. pentosaceus (SC11) fermentation could enhance the anti-allergic potential of C. militaris cultured on germinated Rhynchosia nulubilis (GRC) against a type I hypersensitive reaction in in vitro and in vivo studies. Total antioxidant capacity and cordycepin content were significantly increased in GRC after SC11 fermentation. GRC-SC11 showed significantly enhanced anti-allergic responses by inhibiting immunoglobulin E (IgE)/antigen-induced degranulation in RBL-2H3 cells, compared to GRC. The results demonstrated the significant inhibition of phosphorylated spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk)/ p38/GRB2-associated binding protein 2 (Gab2)/c-jun in IgE/Ag-triggered RBL-2H3 cells. Furthermore, suppressed mRNA levels of interleukin-4 (IL-4) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) in IgE/Ag-activated RBL-2H3 cells were observed. GRC-SC11 significantly ameliorated IgE-induced allergic reactions by suppressing the ear swelling, vascular permeability, and inflammatory cell infiltration in passive cutaneous anaphylaxis (PCA) BALB/c mice. In conclusion, GRC fermented with P.pentosaceus exerted enhanced anti-allergic effects, and increased the cordycepin content and antioxidants potential compared to GRC. It can be used as bio-functional food in the prevention and management of type I allergic diseases.
Keywords: Cordyceps militaris; anti-allergy; fermentation.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest to declare. The funding providers had no role in the study design, execution, or publishing of the manuscript.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Immune-enhancing activity of C. militaris fermented with Pediococcus pentosaceus (GRC-ON89A) in CY-induced immunosuppressed model.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018 Feb 23;18(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s12906-018-2133-9. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018. PMID: 29475435 Free PMC article.
-
Immunostimulatory Activity of Cordyceps militaris Fermented with Pediococcus pentosaceus SC11 Isolated from a Salted Small Octopus in Cyclophosphamide-Induced Immunocompromised Mice and Its Inhibitory Activity against SARS-CoV 3CL Protease.Microorganisms. 2022 Nov 23;10(12):2321. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10122321. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36557573 Free PMC article.
-
Pediococcus pentosaceus-Fermented Cordyceps militaris Inhibits Inflammatory Reactions and Alleviates Contact Dermatitis.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Nov 7;19(11):3504. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113504. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30405049 Free PMC article.
-
A review on polysaccharide biosynthesis in Cordyceps militaris.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Mar;260(Pt 1):129336. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.129336. Epub 2024 Jan 13. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38224811 Review.
-
Research Progress on Cordycepin Synthesis and Methods for Enhancement of Cordycepin Production in Cordyceps militaris.Bioengineering (Basel). 2022 Feb 11;9(2):69. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering9020069. Bioengineering (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35200422 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A randomized controlled clinical trial examining the effects of Cordyceps militaris beverage on the immune response in healthy adults.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 5;14(1):7994. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-58742-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38580687 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Chitosan Nanoparticle-Encapsulated Cordyceps militaris Grown on Germinated Rhynchosia nulubilis Reduces Type II Alveolar Epithelial Cell Apoptosis in PM2.5-Induced Lung Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 27;26(3):1105. doi: 10.3390/ijms26031105. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39940873 Free PMC article.
-
Cordyceps militaris as a Bio Functional Food Source: Pharmacological Potential, Anti-Inflammatory Actions and Related Molecular Mechanisms.Microorganisms. 2022 Feb 10;10(2):405. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10020405. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35208860 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fermented Food in Asthma and Respiratory Allergies-Chance or Failure?Nutrients. 2022 Mar 29;14(7):1420. doi: 10.3390/nu14071420. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35406034 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cordyceps militaris Grown on Germinated Rhynchosia nulubilis (GRC) Encapsulated in Chitosan Nanoparticle (GCN) Suppresses Particulate Matter (PM)-Induced Lung Inflammation in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 3;25(19):10642. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910642. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408971 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Park H.-J., Han E.S., Park D.K., Lee C., Lee K.W. An extract of Phellinus linteus grown on germinated brown rice inhibits inflammation markers in RAW264. 7 macrophages by suppressing inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and mediators and up-regulating antioxidant activity. J. Med. Food. 2010;13:1468–1477. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2010.1131. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Liu S.-N., Han Y., Zhou Z.-J. Lactic acid bacteria in traditional fermented Chinese foods. Food Res. Int. 2011;44:643–651. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2010.12.034. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

