A Comparative Study of the Hepatoprotective Effect of Centella asiatica Extract (CA-HE50) on Lipopolysaccharide/d-galactosamine-Induced Acute Liver Injury in C57BL/6 Mice
- PMID: 34836346
- PMCID: PMC8623393
- DOI: 10.3390/nu13114090
A Comparative Study of the Hepatoprotective Effect of Centella asiatica Extract (CA-HE50) on Lipopolysaccharide/d-galactosamine-Induced Acute Liver Injury in C57BL/6 Mice
Abstract
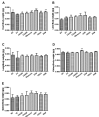
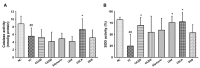
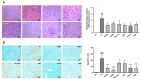
Acute liver failure (ALF) refers to the sudden loss of liver function and is accompanied by several complications. In a previous study, we revealed the protective effect of Centella asiatica 50% ethanol extract (CA-HE50) on acetaminophen-induced liver injury. In the present study, we investigate the hepatoprotective effect of CA-HE50 in a lipopolysaccharide/galactosamine (LPS-D-Gal)-induced ALF animal model and compare it to existing therapeutic silymarin, Lentinus edodes mycelia (LEM) extracts, ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) and dimethyl diphenyl bicarboxylate (DDB). Serum aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels were decreased in the CA-HE50, silymarin, LEM, UDCA and DDB groups compared to the vehicle control group. In particular, AST and ALT levels of the 200 mg/kg CA-HE50 group were significantly decreased compared to positive control groups. Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels were significantly decreased in the CA-HE50, silymarin, LEM, UDCA and DDB groups compared to the vehicle control group and LDH levels of the 200 mg/kg CA-HE50 group were similar to those of the positive control groups. Superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity was significantly increased in the 100 mg/kg CA-HE50, LEM and UDCA groups compared to the vehicle control group and, in particular, the 100 mg/kg CA-HE50 group increased significantly compared to positive control groups. In addition, the histopathological lesion score was significantly decreased in the CA-HE50 and positive control groups compared with the vehicle control group and the histopathological lesion score of the 200 mg/kg CA-HE50 group was similar to that of the positive control groups. These results show that CA-HE50 has antioxidant and hepatoprotective effects at a level similar to that of silymarin, LEM, UDCA and DDB, which are known to have hepatoprotective effects; further, CA-HE50 has potential as a prophylactic and therapeutic agent in ALF.
Keywords: Centella asiatica; acute liver failure; antioxidant; hepatoprotective effect.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Hepatoprotective effect of Centella asiatica 50% ethanol extract against acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury in BALB/c mice.Toxicol Res. 2020 Sep 7;37(2):261-275. doi: 10.1007/s43188-020-00063-0. eCollection 2021 Apr. Toxicol Res. 2020. PMID: 33868982 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of sea buckthorn polysaccharide extracts against LPS/d-GalN-induced acute liver failure in mice via suppressing TLR4-NF-κB signaling.J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Dec 24;176:69-78. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.10.029. Epub 2015 Oct 19. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26494508
-
Hepatoprotective effects of erythropoietin on D-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide-induced fulminant hepatic failure in mice.Mol Med Rep. 2014 Jul;10(1):555-9. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2014.2164. Epub 2014 Apr 24. Mol Med Rep. 2014. PMID: 24788561
-
Are alterations needed in Silybum marianum (Silymarin) administration practices? A novel outlook and meta-analysis on randomized trials targeting liver injury.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2025 Apr 12;25(1):134. doi: 10.1186/s12906-025-04886-y. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2025. PMID: 40221681 Free PMC article.
-
Safety of treating acute liver injury and failure.Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2022 Feb;21(2):191-203. doi: 10.1080/14740338.2021.1955854. Epub 2021 Jul 22. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2022. PMID: 34254839 Review.
Cited by
-
Investigating Protective Effect of Suspension of Paeoniflorin in Combination with Curcumin Against Acute Liver Injury Based on Inhibition of TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 Inflammatory Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 30;26(13):6324. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136324. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40650100 Free PMC article.
-
Medicinal herbs and their metabolites with biological potential to protect and combat liver toxicity and its disorders: A review.Heliyon. 2024 Feb 1;10(3):e25340. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e25340. eCollection 2024 Feb 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38356556 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alleviation of D-gal-induced senile liver injury by Rg3, a signature component of red ginseng.Aging (Albany NY). 2023 Jun 21;15(14):6749-6756. doi: 10.18632/aging.204819. Epub 2023 Jun 21. Aging (Albany NY). 2023. PMID: 37348025 Free PMC article.
-
The Key Molecular Mechanisms of Sini Decoction Plus Ginseng Soup to Rescue Acute Liver Failure: Regulating PPARα to Reduce Hepatocyte Necroptosis?J Inflamm Res. 2022 Aug 22;15:4763-4784. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S373903. eCollection 2022. J Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 36032938 Free PMC article.
-
Centella asiatica: Advances in Extraction Technologies, Phytochemistry, and Therapeutic Applications.Life (Basel). 2025 Jul 9;15(7):1081. doi: 10.3390/life15071081. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40724583 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

