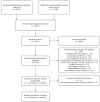
School-Based Nutrition Interventions in Children Aged 6 to 18 Years: An Umbrella Review of Systematic Reviews
- PMID: 34836368
- PMCID: PMC8618558
- DOI: 10.3390/nu13114113
School-Based Nutrition Interventions in Children Aged 6 to 18 Years: An Umbrella Review of Systematic Reviews
Abstract
Schools are identified as a key setting to influence children's and adolescents' healthy eating. This umbrella review synthesised evidence from systematic reviews of school-based nutrition interventions designed to improve dietary intake outcomes in children aged 6 to 18 years. We undertook a systematic search of six electronic databases and grey literature to identify relevant reviews of randomized controlled trials. The review findings were categorised for synthesis by intervention type according to the World Health Organisation Health Promoting Schools (HPS) framework domains: nutrition education; food environment; all three HPS framework domains; or other (not aligned to HPS framework domain). Thirteen systematic reviews were included. Overall, the findings suggest that school-based nutrition interventions, including nutrition education, food environment, those based on all three domains of the HPS framework, and eHealth interventions, can have a positive effect on some dietary outcomes, including fruit, fruit and vegetables combined, and fat intake. These results should be interpreted with caution, however, as the quality of the reviews was poor. Though these results support continued public health investment in school-based nutrition interventions to improve child dietary intake, the limitations of this umbrella review also highlight the need for a comprehensive and high quality systematic review of primary studies.
Keywords: adolescent; child; dietary intake; intervention; nutrition; school-based; umbrella review.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the synthesis, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Consolidating evidence on the effectiveness of interventions promoting fruit and vegetable consumption: an umbrella review.Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2021 Jan 11;18(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s12966-020-01046-y. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2021. PMID: 33430879 Free PMC article.
-
School-based healthy eating interventions for adolescents aged 10-19 years: an umbrella review.Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2024 Oct 14;21(1):117. doi: 10.1186/s12966-024-01668-6. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2024. PMID: 39402562 Free PMC article.
-
Caregiver involvement in interventions for improving children's dietary intake and physical activity behaviors.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 5;1(1):CD012547. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012547.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 31902132 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions for increasing fruit and vegetable consumption in children aged five years and under.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 May 25;5(5):CD008552. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008552.pub7. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Sep 23;9:CD008552. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008552.pub8. PMID: 32449203 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Interventions for increasing fruit and vegetable consumption in children aged five years and under.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Nov 7;2019(11):CD008552. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008552.pub6. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 May 25;5:CD008552. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008552.pub7. PMID: 31697869 Free PMC article. Updated.
Cited by
-
Understanding the Knowledge, Attitudes, and Practices of Healthy Eating among Adolescents in Chongqing, China: An Empirical Study Utilizing Structural Equation Modeling.Nutrients. 2024 Jan 4;16(1):167. doi: 10.3390/nu16010167. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38201997 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying the top 10 research priorities for the school food system in the UK: a priority setting exercise.BMJ Open. 2024 Mar 14;14(3):e081400. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-081400. BMJ Open. 2024. PMID: 38485482 Free PMC article.
-
Improvement of Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet through a Nutrition Education Teaching Pack for Teachers within the "School Fruit Scheme" Program: An Italian Long-Term Trial in School Children.Nutrients. 2024 Jun 27;16(13):2057. doi: 10.3390/nu16132057. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38999804 Free PMC article.
-
Associated factors of dietary diversity among schoolchildren in Plateau Central region of Burkina Faso: a cross-sectional study.BMC Nutr. 2024 Jun 25;10(1):91. doi: 10.1186/s40795-024-00896-0. BMC Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38918872 Free PMC article.
-
Improving the adoption of a school-based nutrition program: findings from a collaborative network of randomised trials.Implement Sci. 2025 Jan 16;20(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s13012-025-01417-8. Implement Sci. 2025. PMID: 39819778 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Roth G.A., Mensah G.A., Johnson C.O., Addolorato G., Ammirati E., Baddour L.M., Barengo N.C., Beaton A.Z., Benjamin E.J., Benziger C.P., et al. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors, 1990–2019: Update From the GBD 2019 Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020;76:2982–3021. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.11.010. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- WHO. FAO . Strengthening Nutrition Action: A Resource Guide for Countries Based on the Policy Recommendations of the Second International Conference on Nutrition (ICN2) World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; Rome, Italy: 2018.
-
- Fleming C.A., Hockey K., Schmied V., Third A., De Oliveira J.D. Food and Me. How Adolescents Experience Nutrition across the World. A Companion Report to The State of the World’s Children. Western Sydney University; Penrith, Australia: United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF); New York, NY, USA: 2019. - DOI
-
- Jacob M.J., Baird J., Barker M., Cooper C., Hanson M. The Importance of a Life-Course Approach to Health: Chronic Disease Risk from Preconception through Adolescence and Adulthood: White Paper. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2017.
-
- UNICEF . The State of the World’s Children 2019. Children, Food and Nutrition: Growing Well in a Changing World. United Nations Children’s Fund; New York, NY, USA: 2019.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical