Monitoring calcium handling by the plant endoplasmic reticulum with a low-Ca2+ -affinity targeted aequorin reporter
- PMID: 34837294
- PMCID: PMC9299891
- DOI: 10.1111/tpj.15610
Monitoring calcium handling by the plant endoplasmic reticulum with a low-Ca2+ -affinity targeted aequorin reporter
Abstract
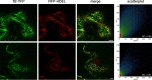
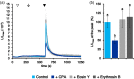
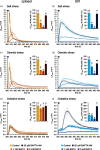
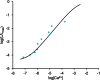
Precise measurements of dynamic changes in free Ca2+ concentration in the lumen of the plant endoplasmic reticulum (ER) have been lacking so far, despite increasing evidence for the contribution of this intracellular compartment to Ca2+ homeostasis and signalling in the plant cell. In the present study, we targeted an aequorin chimera with reduced Ca2+ affinity to the ER membrane and facing the ER lumen. To this aim, the cDNA for a low-Ca2+ -affinity aequorin variant (AEQmut) was fused to the nucleotide sequence encoding a non-cleavable N-terminal ER signal peptide (fl2). The correct targeting of fl2-AEQmut was confirmed by immunocytochemical analyses in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana (Arabidopsis) seedlings. An experimental protocol well-established in animal cells - consisting of ER Ca2+ depletion during photoprotein reconstitution followed by ER Ca2+ refilling - was applied to carry out ER Ca2+ measurements in planta. Rapid and transient increases of the ER luminal Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+ ]ER ) were recorded in response to different environmental stresses, displaying stimulus-specific Ca2+ signatures. The comparative analysis of ER and chloroplast Ca2+ dynamics indicates a complex interplay of these organelles in shaping cytosolic Ca2+ signals during signal transduction events. Our data highlight significant differences in basal [Ca2+ ]ER and Ca2+ handling by plant ER compared to the animal counterpart. The set-up of an ER-targeted aequorin chimera extends and complements the currently available toolkit of organelle-targeted Ca2+ indicators by adding a reporter that improves our quantitative understanding of Ca2+ homeostasis in the plant endomembrane system.
Keywords: Arabidopsis thaliana; aequorin; calcium homeostasis; chloroplasts; endoplasmic reticulum; environmental stresses; signal transduction.
© 2021 The Authors. The Plant Journal published by Society for Experimental Biology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Alonso, M.T. , Rodríguez‐Prados, M. , Navas‐Navarro, P. , Rojo‐Ruiz, J. & García‐Sancho, J. (2017) Using aequorin probes to measure Ca2+ in intracellular organelles. Cell Calcium, 64, 3–11. - PubMed
-
- Baker, C.J. & Mock, N.M. (1994) An improved method for monitoring cell death in cell suspension and leaf disc assays using evans blue. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture, 39, 7–12.
-
- Bayer, E.M. , Sparkes, I. , Vanneste, S. & Rosado, A. (2017) From shaping organelles to signalling platforms: the emerging functions of plant ER‐PM contact sites. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 40, 89–96. - PubMed
-
- Berridge, M.J. , Lipp, P. & Bootman, M.D. (2000) The versatility and universality of calcium signalling. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 1, 11–21. - PubMed
-
- Block, M.A. & Jouhet, J. (2015) Lipid trafficking at endoplasmic reticulum‐chloroplast membrane contact sites. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 35, 21–29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

