The RavA/VemR two-component system plays vital regulatory roles in the motility and virulence of Xanthomonas campestris
- PMID: 34837306
- PMCID: PMC8828458
- DOI: 10.1111/mpp.13164
The RavA/VemR two-component system plays vital regulatory roles in the motility and virulence of Xanthomonas campestris
Abstract
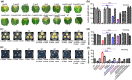
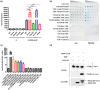
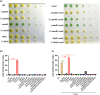
Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris (Xcc) can cause black rot in cruciferous plants worldwide. Two-component systems (TCSs) are key for bacterial adaptation to various environments, including hosts. VemR is a TCS response regulator and crucial for Xcc motility and virulence. Here, we report that RavA is the cognate histidine kinase (HK) of VemR and elucidate the signalling pathway by which VemR regulates Xcc motility and virulence. Genetic analysis showed that VemR is epistatic to RavA. Using bacterial two-hybrid experiments and pull-down and phosphorylation assays, we found that RavA can interact with and phosphorylate VemR, suggesting that RavA is the cognate HK of VemR. In addition, we found that RpoN2 and FleQ are epistatic to VemR in regulating bacterial motility and virulence. In vivo and in vitro experiments demonstrated that VemR interacts with FleQ but not with RpoN2. RavA/VemR regulates the expression of the flagellin-encoding gene fliC by activating the transcription of the rpoN2-vemR-fleQ and flhF-fleN-fliA operons. In summary, our data show that the RavA/VemR TCS regulates FleQ activity and thus influences the expression of motility-related genes, thereby affecting Xcc motility and virulence. The identification of this novel signalling pathway will deepen our understanding of Xcc-plant interactions.
Keywords: RavA/VemR; motility; signalling pathway; two-component system; virulence.
© 2021 The Authors. Molecular Plant Pathology published by British Society for Plant Pathology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures


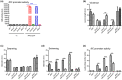
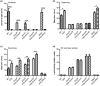
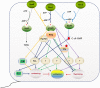
 positive regulation;
positive regulation;  negative regulation; solid lines, having experimental evidence; dotted lines, supposed relationship. Components of a given pathway are indicated in the same colour
negative regulation; solid lines, having experimental evidence; dotted lines, supposed relationship. Components of a given pathway are indicated in the same colourSimilar articles
-
Xanthomonas campestris VemR enhances the transcription of the T3SS key regulator HrpX via physical interaction with HrpG.Mol Plant Pathol. 2023 Mar;24(3):232-247. doi: 10.1111/mpp.13293. Epub 2023 Jan 10. Mol Plant Pathol. 2023. PMID: 36626275 Free PMC article.
-
Response regulator, VemR, positively regulates the virulence and adaptation of Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2010 Mar;304(1):20-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2010.01892.x. Epub 2010 Jan 15. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2010. PMID: 20082640
-
Xanthomonas campestris sensor kinase HpaS co-opts the orphan response regulator VemR to form a branched two-component system that regulates motility.Mol Plant Pathol. 2020 Mar;21(3):360-375. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12901. Epub 2020 Jan 9. Mol Plant Pathol. 2020. PMID: 31919999 Free PMC article.
-
The roles of histidine kinases in sensing host plant and cell-cell communication signal in a phytopathogenic bacterium.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2019 Mar 4;374(1767):20180311. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2018.0311. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30967026 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of Two-Component Signal Transduction Systems in Shigella Virulence.Biomolecules. 2022 Sep 18;12(9):1321. doi: 10.3390/biom12091321. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36139160 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Xanthomonas campestris VemR enhances the transcription of the T3SS key regulator HrpX via physical interaction with HrpG.Mol Plant Pathol. 2023 Mar;24(3):232-247. doi: 10.1111/mpp.13293. Epub 2023 Jan 10. Mol Plant Pathol. 2023. PMID: 36626275 Free PMC article.
-
Xanthomonas oryzae Pv. oryzicola Response Regulator VemR Is Co-opted by the Sensor Kinase CheA for Phosphorylation of Multiple Pathogenicity-Related Targets.Front Microbiol. 2022 Jun 9;13:928551. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.928551. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35756024 Free PMC article.
-
The pathogenicity-associated regulators participating in the regulatory cascade for RaxSTAB and RaxX in Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae.Mol Plant Pathol. 2024 Nov;25(11):e70025. doi: 10.1111/mpp.70025. Mol Plant Pathol. 2024. PMID: 39529415 Free PMC article.
-
A transcriptional Regulator Gar Regulates the Growth and Virulence of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae.Curr Microbiol. 2023 Jul 12;80(9):279. doi: 10.1007/s00284-023-03396-9. Curr Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37436661
-
Functional study of FleQ reveals the co-regulation of flgG by rpoN2vemRfleQ operon members in Xanthomonas citri subsp. citri.iScience. 2025 Jun 19;28(7):112960. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112960. eCollection 2025 Jul 18. iScience. 2025. PMID: 40687810 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Appleby, J.L. & Bourret, R.B. (1999) Activation of CheY mutant D57N by phosphorylation at an alternative site, Ser‐56. Molecular Microbiology, 34, 915–925. - PubMed
-
- Bardy, S.L. , Ng, S.Y. & Jarrell, K.F. (2003) Prokaryotic motility structures. Microbiology, 149, 295–304. - PubMed
-
- Berg, H.C. (2003) The rotary motor of bacterial flagella. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 72, 19–54. - PubMed
-
- Buschiazzo, A. & Trajtenberg, F. (2019) Two‐component sensing and regulation: how do histidine kinases talk with response regulators at the molecular level? Annual Review of Microbiology, 73, 507–528. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

