Global Scientific Research on SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines: A Bibliometric Analysis
- PMID: 34837679
- PMCID: PMC8588811
- DOI: 10.22074/cellj.2021.7794
Global Scientific Research on SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines: A Bibliometric Analysis
Abstract
Objective: We performed this bibliometric analysis to identify global scientific research on the SARS-CoV-2 vaccines.
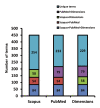
Materials and methods: This bibliometric analysis study inclusive search of English-language publications related to the SARS-CoV-2 vaccines was conducted in the Scopus, PubMed, and Dimensions databases without year limitations. The results of bibliometric analysis comprised a time-dependent citation density trend, the name of the journal, journal impact factor (IF), year of publication, type of article, category, subscription or affiliation, co-authorship, and cooccurrence network.
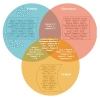
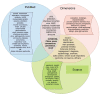
Results: A study of the scientific literature from three databases (Scopus, PubMed, Dimensions) shows that investigators have focused more on studying the structure of the coronavirus at different levels (organismic, cellular, and molecular). In addition, the method of virus penetration into the cell and features of the influence of coronavirus on animals are well-studied. Various methods and strategies are being used to develop the vaccines, including both animal-tested methods and computer models. The Dimensions database is the most representative in terms of coverage of research on development of the SARS-CoV-2 vaccines.
Conclusion: This research is a scientific investigation based on bibliometric analysis of papers related to the SARS-CoV-2 vaccines. The Dimensions database provides the most representative research coverage on the creation of a vaccine against coronavirus. It is characterized by a large number of formed verbose terms (length of more than four words) related to coronavirus, which makes it possible to track trends in the development of methods for creating a vaccine.
Keywords: Bibliometric Analysis; COVID-19/SARS-CoV-2; Vaccine.
Copyright© by Royan Institute. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest in this study.
Figures
References
-
- Scudellari M. How the pandemic might play out in 2021 and beyond.Nature.Available from: https://www.nature. com/articles/ d41586-020-02278-5. 2020 05 Aug 2020. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
