Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 inhibits the acetylation of PTEN through the miR-524-5p /HDAC1 axis to promote the proliferation and invasion of laryngeal cancer cells
- PMID: 34837887
- PMCID: PMC8660614
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.203719
Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 inhibits the acetylation of PTEN through the miR-524-5p /HDAC1 axis to promote the proliferation and invasion of laryngeal cancer cells
Abstract
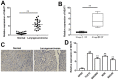
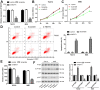
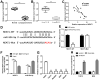
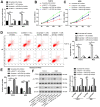
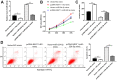
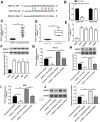
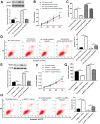
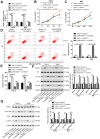
Long noncoding RNA nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 (lncRNA NEAT1) is abnormally expressed in numerous tumors and functions as an oncogene, but the role of NEAT1 in laryngocarcinoma is largely unknown. Our study validated that NEAT1 expression was markedly upregulated in laryngocarcinoma tissues and cells. Downregulation of NEAT1 dramatically suppressed cell proliferation and invasion through inhibiting miR-524-5p expression. Additionally, NEAT1 overexpression promoted cell growth and metastasis, while overexpression of miR-524-5p could reverse the effect. NEAT1 increased the expression of histone deacetylase 1 gene (HDAC1) via sponging miR-524-5p. Mechanistically, overexpression of HDAC1 recovered the cancer-inhibiting effects of miR-524-5p mimic or NEAT1 silence by deacetylation of tensin homolog deleted on chromosome ten (PTEN) and inhibiting AKT signal pathway. Moreover, in vivo experiments indicated that silence of NEAT1 signally suppressed tumor growth. Taken together, knockdown of NEAT1 suppressed laryngocarcinoma cell growth and metastasis by miR-524-5p/HDAC1/PTEN/AKT signal pathway, which provided a potential therapeutic target for laryngocarcinoma.
Keywords: histone deacetylationase 1; laryngocarcinoma; long noncoding RNA nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1; miR-524-5p; phosphatase and tensin homolog /protein kinase B signaling pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Long noncoding RNA nuclear enriched abundant transcript 1 impacts cell proliferation, invasion, and migration of glioma through regulating miR-139-5p/ CDK6.J Cell Physiol. 2019 May;234(5):5972-5987. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27093. Epub 2018 Dec 4. J Cell Physiol. 2019. Retraction in: J Cell Physiol. 2023 Feb;238(2):478. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30962. PMID: 30515782 Retracted.
-
Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 promotes the growth of cervical cancer cells via sponging miR-9-5p.Biochem Cell Biol. 2019 Apr;97(2):100-108. doi: 10.1139/bcb-2018-0111. Epub 2018 Aug 10. Biochem Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 30096244
-
Mechanism of miR-340-5p in laryngeal cancer cell proliferation and invasion through the lncRNA NEAT1/MMP11 axis.Pathol Res Pract. 2022 Aug;236:153912. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2022.153912. Epub 2022 Apr 29. Pathol Res Pract. 2022. PMID: 35700579
-
An overview of lncRNA NEAT1 contribution in the pathogenesis of female cancers; from diagnosis to therapy resistance.Gene. 2025 Jan 15;933:148975. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2024.148975. Epub 2024 Sep 29. Gene. 2025. PMID: 39353536 Review.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Tumorgenesis and Metastasis of Long Non-coding RNA (lncRNA) NEAT1 in Human Solid Tumors; An Update.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024 Jun;82(2):593-607. doi: 10.1007/s12013-024-01287-9. Epub 2024 May 15. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024. PMID: 38750383 Review.
Cited by
-
Long non-coding RNA nuclear enriched abundant transcript 1 (NEAT1) modulates inhibitor of DNA binding 1 (ID1) to facilitate papillary thyroid carcinoma development by sponging microRNA-524-5p.Bioengineered. 2022 May;13(5):13201-13212. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2076498. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35635748 Free PMC article.
-
Histone Modifications and Non-Coding RNAs: Mutual Epigenetic Regulation and Role in Pathogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 22;23(10):5801. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105801. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35628612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 promotes aerobic glycolysis and progression of cervical cancer through WNT/β-catenin/PDK1 axis.Cancer Med. 2024 May;13(9):e7221. doi: 10.1002/cam4.7221. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 38733179 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of microRNAs in Patients with Laryngeal Cancer: A Systematic Review.Noncoding RNA. 2023 Jan 19;9(1):9. doi: 10.3390/ncrna9010009. Noncoding RNA. 2023. PMID: 36827542 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasma Circulating lncRNAs: MALAT1 and NEAT1 as Biomarkers of Radiation-Induced Adverse Effects in Laryngeal Cancer Patients.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Mar 10;15(6):676. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15060676. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40150019 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhao F, Huang W, Ousman T, Zhang B, Han Y, Clotaire DZ, Wang C, Chang H, Luo H, Ren X, Lei M. Triptolide induces growth inhibition and apoptosis of human laryngocarcinoma cells by enhancing p53 activities and suppressing E6-mediated p53 degradation. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e80784. 10.1371/journal.pone.0080784 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

