The Progress of Medical Image Semantic Segmentation Methods for Application in COVID-19 Detection
- PMID: 34840563
- PMCID: PMC8611358
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/7265644
The Progress of Medical Image Semantic Segmentation Methods for Application in COVID-19 Detection
Abstract
Image medical semantic segmentation has been employed in various areas, including medical imaging, computer vision, and intelligent transportation. In this study, the method of semantic segmenting images is split into two sections: the method of the deep neural network and previous traditional method. The traditional method and the published dataset for segmentation are reviewed in the first step. The presented aspects, including all-convolution network, sampling methods, FCN connector with CRF methods, extended convolutional neural network methods, improvements in network structure, pyramid methods, multistage and multifeature methods, supervised methods, semiregulatory methods, and nonregulatory methods, are then thoroughly explored in current methods based on the deep neural network. Finally, a general conclusion on the use of developed advances based on deep neural network concepts in semantic segmentation is presented.
Copyright © 2021 Amin Valizadeh and Morteza Shariatee.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



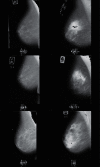







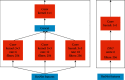
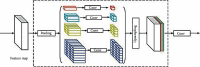


References
-
- Thoma M. A survey of semantic segmentation. 2016. http://arxiv.org/abs/1602.06541 .
-
- Rezaei M., Farahanipad F., Dillhoff A., Elmasri R., Athitsos V. Weakly-supervised hand part segmentation from depth images. Proceedings of the 14th PErvasive Technologies Related to Assistive Environments Conference; June 2021; Corfu, Greece. pp. 218–225. - DOI
-
- Li Y., Qi H., Dai J., Ji X., Wei Y. Fully convolutional instance-aware semantic segmentation. Proceedings of the 30th IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; July 2017; Honolulu, HI, USA. pp. 4438–4446. - DOI
-
- Maldonado-Bascon S., Lafuente-Arroyo S., Gil-Jimenez P., Gomez-Moreno H., Lopez-Ferreras F. Road-sign detection and recognition based on support vector machines. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems . 2007;8(2):264–278. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2007.895311. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

