Systemic sclerosis cutaneous expression: Management of skin fibrosis and digital ulcers
- PMID: 34840747
- PMCID: PMC8606707
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amsu.2021.102984
Systemic sclerosis cutaneous expression: Management of skin fibrosis and digital ulcers
Abstract
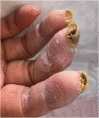
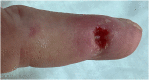
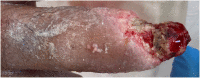
Systemic sclerosis is a connective tissue disease with cutaneous involvement. Clinical manifestations result from the balance of inflammations/autoimmunity process and fibrogenesis. Patients suffer from skin ulcers, non-ulcerative lesions including digital pitting scars, telangiectasias, subungual hyperkeratosis, abrasions, fissures, and subcutaneous calcinosis. A review about the pathophysiology of the disease, the physical examination of the patients, the instrumental assessment, and possible treatments is performed.
Keywords: Autologous fat grafting; DU, digital ulcer; Digital ulcers; MHISS, Mouth Handicap in Systemic Sclerosis scale; ROM, Range of Motion; RP, Raynaud's phenomenon; SSc, Systemic sclerosis; SU, skin ulcer; Scleroderma; Skin fibrosis; Systemic sclerosis.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declares that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Giuggioli D., Manfredi A., Colaci M., Manzini C.U., Antonelli A., Ferri C. Systemic sclerosis and cryoglobulinemia: our experience with overlapping syndrome of scleroderma and severe cryoglobulinemic vasculitis and review of the literature. Autoimmun Rev. 2013 Sep;12(11):1058–1063. - PubMed
-
- Ferri C., Sebastiani M., Lo Monaco A., Iudici M., Giuggioli D., Furini F., et al. Systemic sclerosis evolution of disease pathomorphosis and survival. Our experience on Italian patients' population and review of the literature. Autoimmun Rev. 2014 Oct;13(10):1026–1034. - PubMed
-
- Ferri C., Giuggioli D., Guiducci S., Lumetti F., Bajocchi G., Magnani L., et al. Systemic sclerosis Progression INvestiGation (SPRING) Italian registry: demographic and clinico-serological features of the scleroderma spectrum. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2020 Jun;38(Suppl 125):40–47. (3) - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources