Decreasing Emergency Department Visits for Children With Epilepsy
- PMID: 34840868
- PMCID: PMC8610546
- DOI: 10.1212/CPJ.0000000000001109
Decreasing Emergency Department Visits for Children With Epilepsy
Abstract
Background and objectives: Epilepsy and seizures represent a frequent cause of emergency department (ED) visits for patients. By implementing quality improvement (QI) methodology, we planned to decrease ED visits for children and adolescents with epilepsy.
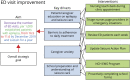
Methods: In 2016, a multidisciplinary team was created to implement QI methodology to address ED visits for patients with epilepsy. Based on previous successes, further ED visit reduction was deemed possible. Our aim statement was to decrease the number of ED visits, per 1000 established patients with epilepsy, from 13.03 to 11.6, by December 2019 and sustain for 1 year.
Results: We successfully decreased ED visits for seizure-related care in patients with epilepsy from 13.03% to 10.2% per 1,000 patients, which resulted in a centerline shift.
Discussion: Using QI methodology, we improved the outcome measure of decreasing ED visits for children with epilepsy. Implementations of these interventions can be considered at other institutions that may lead to similar results.
© 2021 American Academy of Neurology.
Figures
References
-
- Burrows L, Lennard S, Hudson S, et al. . Exploring epilepsy attendance at the emergency department and interventions which may reduce unnecessary attendances: a scoping review. Seizure. 2020;76:39-46. - PubMed
-
- Grinspan ZM, Patel AD, Hafeez B, Abramson EL, Kern LM. Predicting frequent emergency department use among children with epilepsy: a retrospective cohort study using electronic health data from 2 centers. Epilepsia. 2018;59(1):155-169. - PubMed
-
- Lekoubou A, Bishu KG, Ovbiagele B. Nationwide Healthcare utilization among children with epilepsy in the United States: 2003-2014. Epilepsy Res. 2018;141:90-94. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources