Combining Network Pharmacology with Molecular Docking for Mechanistic Research on Thyroid Dysfunction Caused by Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers and Their Metabolites
- PMID: 34840968
- PMCID: PMC8613503
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/2961747
Combining Network Pharmacology with Molecular Docking for Mechanistic Research on Thyroid Dysfunction Caused by Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers and Their Metabolites
Abstract
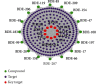
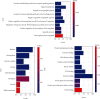
Network pharmacology was used to illuminate the targets and pathways of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) causing thyroid dysfunction. A protein-protein interaction (PPI) network was constructed. Molecular docking was applied to analyze PBDEs and key targets according to the network pharmacology results. A total of 247 targets were found to be related to 16 PBDEs. Ten key targets with direct action were identified, including the top five PIK3R1, MAPK1, SRC, RXRA, and TP53. Gene Ontology (GO) functional enrichment analysis identified 75 biological items. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analysis identified 62 pathways mainly related to the regulation of the thyroid hormone signaling pathway, MAPK signaling pathway, PI3K-Akt signaling, pathways in cancer, proteoglycans in cancer, progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation, and others. The molecular docking results showed that BDE-99, BDE-153, 5-OH-BDE47, 5'-OH-BDE99, 5-BDE47 sulfate, and 5'-BDE99 sulfate have a good binding effect with the kernel targets. PBDEs could interfere with the thyroid hormone endocrine through multiple targets and biological pathways, and metabolites demonstrated stronger effects than the prototypes. This research provides a basis for further research on the toxicological effects and molecular mechanisms of PBDEs and their metabolites. Furthermore, the application of network pharmacology to the study of the toxicity mechanisms of environmental pollutants provides a new methodology for environmental toxicology.
Copyright © 2021 Qiaoyu He et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures



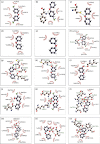
 = ligand bond;
= ligand bond;  = nonligand bond;
= nonligand bond;  = hydrogen bond and its length;
= hydrogen bond and its length;  = nonligand residues involved in hydrophobic contact(s);
= nonligand residues involved in hydrophobic contact(s);  = corresponding atoms involved in hydrophobic contact(s)).
= corresponding atoms involved in hydrophobic contact(s)).References
-
- Chen X. P., Lin Y. P., Dang K., Puschner B. Quantification of polychlorinated biphenyls and polybrominated diphenyl ethers in commercial cows’ milk from California by gas chromatography-triple quadruple mass spectrometry. PloS one . 2017;12(1, article e0170129) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0170129. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stapleton H. M., Eagle S., Anthopolos R., Wolkin A., Miranda M. L. Associations between polybrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE) flame retardants, phenolic metabolites, and thyroid hormones during pregnancy. Environmental Health Perspectives . 2011;119(10):1454–1459. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1003235. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zota A. R., Park J. S., Wang Y., Petreas M., Zoeller T. R., Woodruff T. J. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers, hydroxylated polybrominated diphenyl ethers, and measures of thyroid function in second trimester pregnant women in California. Environmental Science & Technology . 2011;45(18):7896–7905. doi: 10.1021/es200422b. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

