The mRNA-LNP platform's lipid nanoparticle component used in preclinical vaccine studies is highly inflammatory
- PMID: 34841223
- PMCID: PMC8604799
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.103479
The mRNA-LNP platform's lipid nanoparticle component used in preclinical vaccine studies is highly inflammatory
Abstract
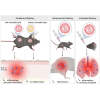
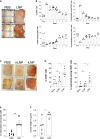
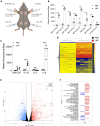
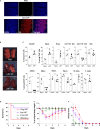
Vaccines based on mRNA-containing lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) are a promising new platform used by two leading vaccines against COVID-19. Clinical trials and ongoing vaccinations present with varying degrees of protection levels and side effects. However, the drivers of the reported side effects remain poorly defined. Here we present evidence that Acuitas' LNPs used in preclinical nucleoside-modified mRNA vaccine studies are highly inflammatory in mice. Intradermal and intramuscular injection of these LNPs led to rapid and robust inflammatory responses, characterized by massive neutrophil infiltration, activation of diverse inflammatory pathways, and production of various inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. The same dose of LNP delivered intranasally led to similar inflammatory responses in the lung and resulted in a high mortality rate, with mechanism unresolved. Thus, the mRNA-LNP platforms' potency in supporting the induction of adaptive immune responses and the observed side effects may stem from the LNPs' highly inflammatory nature.
Keywords: Biological sciences; Biotechnology; Immunology.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflict of any sort.
Figures

Update of
-
The mRNA-LNP platform's lipid nanoparticle component used in preclinical vaccine studies is highly inflammatory.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2021 Jul 23:2021.03.04.430128. doi: 10.1101/2021.03.04.430128. bioRxiv. 2021. Update in: iScience. 2021 Dec 17;24(12):103479. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.103479. PMID: 33688649 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Bernasconi V., Norling K., Gribonika I., Ong L.C., Burazerovic S., Parveen N., Schön K., Stensson A., Bally M., Larson G., et al. A vaccine combination of lipid nanoparticles and a cholera toxin adjuvant derivative greatly improves lung protection against influenza virus infection. Mucosal Immunol. 2021;14:523–536. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

