Novel patient-derived models of desmoplastic small round cell tumor confirm a targetable dependency on ERBB signaling
- PMID: 34841430
- PMCID: PMC8807576
- DOI: 10.1242/dmm.047621
Novel patient-derived models of desmoplastic small round cell tumor confirm a targetable dependency on ERBB signaling
Abstract
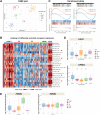
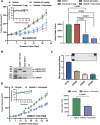
Desmoplastic small round cell tumor (DSRCT) is characterized by the t(11;22)(p13;q12) translocation, which fuses the transcriptional regulatory domain of EWSR1 with the DNA-binding domain of WT1, resulting in the oncogenic EWSR1-WT1 fusion protein. The paucity of DSRCT disease models has hampered preclinical therapeutic studies on this aggressive cancer. Here, we developed preclinical disease models and mined DSRCT expression profiles to identify genetic vulnerabilities that could be leveraged for new therapies. We describe four DSRCT cell lines and one patient-derived xenograft model. Transcriptomic, proteomic and biochemical profiling showed evidence of activation of the ERBB pathway. Ectopic expression of EWSR1-WT1 resulted in upregulation of ERRB family ligands. Treatment of DSRCT cell lines with ERBB ligands resulted in activation of EGFR, ERBB2, ERK1/2 and AKT, and stimulation of cell growth. Antagonizing EGFR function with shRNAs, small-molecule inhibitors (afatinib, neratinib) or an anti-EGFR antibody (cetuximab) inhibited proliferation of DSRCT cells. Finally, treatment of mice bearing DSRCT xenografts with a combination of cetuximab and afatinib significantly reduced tumor growth. These data provide a rationale for evaluating EGFR antagonists in patients with DSRCT. This article has an associated First Person interview with the joint first authors of the paper.
Keywords: DSRCT PDX; EGFR; EWSR1-WT1; Sarcoma proteomics.
© 2022. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests R.S.S., I.O., Z.L., A.J.-W.L., T.H., M.V., Y.S., L.D., M.S.M., H.A.R., M.S., G.B., A.B.H., E.G., S.K., H.M., I.K., E.D.S., M.P.L.Q., J.Y., M. Laé, S.B.L. and L.S. report no potential competing interest. J.H. is a Scientific Editor at DMM but was not included in any aspect of the editorial handling of this article. C.A.P. has received consulting fees from Genentech/Roche and receives research funding from Kura Oncology for studies not related to this paper. M. Ladanyi has received advisory board compensation from Boehringer Ingelheim, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Takeda, Bayer and Paige.AI, and research support from LOXO Oncology, Helsinn Healthcare, Elevation Oncology and Merus. R.S. has received research grants from Merus, Helsinn Healthcare, LOXO Oncology and Elevation Oncology for studies unrelated to this paper.
Figures






References
-
- Cheng, D. T., Mitchell, T. N., Zehir, A., Shah, R. H., Benayed, R., Syed, A., Chandramohan, R., Liu, Z. Y., Won, H. H., Scott, S. N.et al. (2015). Memorial Sloan Kettering-integrated mutation profiling of actionable cancer targets (MSK-IMPACT): A hybridization capture-based next-generation sequencing clinical assay for solid tumor molecular oncology. J. Mol. Diagn., 17, 251-264. 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2014.12.006 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Filion, C., Motoi, T., Olshen, A. B., Lae, M., Emnett, R. J., Gutmann, D. H., Perry, A., Ladanyi, M. and Labelle, Y. (2009). The EWSR1/NR4A3 fusion protein of extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma activates the PPARG nuclear receptor gene. J. Pathol., 217, 83-93. 10.1002/path.2445 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

