New focuses on roles of communications between endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria in identification of biomarkers and targets
- PMID: 34841708
- PMCID: PMC8562589
- DOI: 10.1002/ctm2.626
New focuses on roles of communications between endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria in identification of biomarkers and targets
Abstract
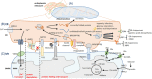
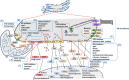
The communication between endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and mitochondria (Mt) plays important roles in maintenance of intra- and extra-cellular microenvironment, metabolisms, signaling activities and cell-cell communication. The present review aims to overview the advanced understanding about roles of ER-Mt structural contacts, molecular interactions and chemical exchanges, signal transmissions and inter-organelle regulations in ER-Mt communication. We address how the ER-Mt communication contributes to the regulation of lipid, amino acid and glucose metabolisms by enzymes, transporters and regulators in the process of biosynthesis. We specially emphasize the importance of deep understanding about molecular mechanisms of ER-Mt communication for identification and development of biology-specific, disease-specific and metabolism-specific biomarkers and therapeutic targets for human diseases. The inhibitors and modulators of the ER-Mt communication are categorized according to therapeutic targets. Rapid development of biotechnologies will provide new insights for spatiotemporally understanding the molecular mechanisms of ER-Mt communication.
Keywords: communications; contacts; diseases; endoplasmic reticulum; homeostasis; mitochondria.
© 2021 The Authors. Clinical and Translational Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Shanghai Institute of Clinical Bioinformatics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Figures


References
-
- Song D, Yang D, Powell CA, Wang X. Cell‐cell communication: old mystery and new opportunity. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2019;35:89‐93. - PubMed
-
- Bernhard W, Haguenau F, Gautier A, Oberling C. Submicroscopical structure of cytoplasmic basophils in the liver, pancreas and salivary gland; study of ultrafine slices by electron microscope. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1952;37:281‐300. - PubMed
-
- Vance JE. Phospholipid synthesis in a membrane fraction associated with mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:7248‐7256. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81873409/Operation Funding of Shanghai Institute of Clinical Bioinformatics and Shanghai Engineering and Technology Center for Artificial Intelligence of Lung and Heart Diseases from Zhongshan Hospital, The National Nature Science Foundation of China
- 2017YFC0909500/National Key Research and Development Program of Precision Medicine
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
