Eplerenone nanocrystals engineered by controlled crystallization for enhanced oral bioavailability
- PMID: 34842018
- PMCID: PMC8635601
- DOI: 10.1080/10717544.2021.2008051
Eplerenone nanocrystals engineered by controlled crystallization for enhanced oral bioavailability
Abstract
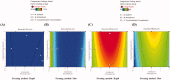
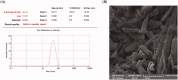
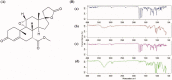
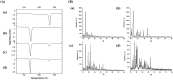
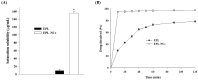
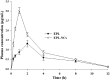
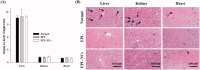
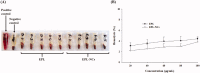
Poor aqueous solubility of eplerenone (EPL) is a major obstacle to achieve sufficient bioavailability after oral administration. In this study, we aimed to develop and evaluate eplerenone nanocrystals (EPL-NCs) for solubility and dissolution enhancement. D-optimal combined mixture process using Design-Expert software was employed to generate different combinations for optimization. EPL-NCs were prepared by a bottom-up, controlled crystallization technique during freeze-drying. The optimized EPL-NCs were evaluated for their size, morphology, thermal behavior, crystalline structure, saturation solubility, dissolution profile, in vivo pharmacokinetics, and acute toxicity. The optimized EPL-NCs showed mean particle size of 46.8 nm. Scanning electron microscopy revealed the formation of elongated parallelepiped shaped NCs. DSC and PXRD analysis confirmed the crystalline structure and the absence of any polymorphic transition in EPL-NCs. Furthermore, EPL-NCs demonstrated a 17-fold prompt increase in the saturation solubility of EPL (8.96 vs. 155.85 µg/mL). The dissolution rate was also significantly higher as indicated by ∼95% dissolution from EPL-NCs in 10 min compared to only 29% from EPL powder. EPL-NCs improved the oral bioavailability as indicated by higher AUC, Cmax, and lower Tmax than EPL powder. Acute oral toxicity study showed that EPL-NCs do not pose any toxicity concern to the blood and vital organs. Consequently, NCs prepared by controlled crystallization technique present a promising strategy to improve solubility profile, dissolution velocity and bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs.
Keywords: Eplerenone; acute toxicity study; controlled crystallization; dissolution rate and bioavailability; nanocrystals; poorly aqueous solubility.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflict of interests in the current study.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lipid-based nano-formulation platform for eplerenone oral delivery as a potential treatment of chronic central serous chorioretinopathy: in-vitro optimization and ex-vivo assessment.Drug Deliv. 2021 Dec;28(1):642-654. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2021.1902023. Drug Deliv. 2021. PMID: 33787445 Free PMC article.
-
Development of posaconazole nanocrystalline solid dispersion: preparation, characterization and in vivo evaluation.Pharm Dev Technol. 2024 Jun;29(5):530-540. doi: 10.1080/10837450.2024.2353314. Epub 2024 May 28. Pharm Dev Technol. 2024. PMID: 38713634
-
Development of surface stabilized candesartan cilexetil nanocrystals with enhanced dissolution rate, permeation rate across CaCo-2, and oral bioavailability.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2016 Oct;6(5):498-510. doi: 10.1007/s13346-016-0297-8. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2016. PMID: 27129488
-
Nanocrystals based pulmonary inhalation delivery system: advance and challenge.Drug Deliv. 2022 Dec;29(1):637-651. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2022.2039809. Drug Deliv. 2022. PMID: 35188021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanocrystals: A Deep Insight into Formulation Aspects, Stabilization Strategies, and Biomedical Applications.Recent Pat Nanotechnol. 2023;17(4):307-326. doi: 10.2174/1872210516666220523120313. Recent Pat Nanotechnol. 2023. PMID: 35616680 Review.
Cited by
-
QbD Approach for the Development of Tea Tree Oil-Enhanced Microemulgel Loaded with Curcumin and Diclofenac for Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment.Gels. 2024 Sep 30;10(10):634. doi: 10.3390/gels10100634. Gels. 2024. PMID: 39451289 Free PMC article.
-
Augmented Oral Bioavailability and Prokinetic Activity of Levosulpiride Delivered in Nanostructured Lipid Carriers.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Oct 31;14(11):2347. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14112347. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36365165 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced Antidepressant Activity of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers Containing Levosulpiride in Behavioral Despair Tests in Mice.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Aug 29;16(9):1220. doi: 10.3390/ph16091220. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37765028 Free PMC article.
-
Formulation and Evaluation of a Self-Microemulsifying Drug Delivery System of Raloxifene with Improved Solubility and Oral Bioavailability.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Aug 2;15(8):2073. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15082073. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37631288 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aksoylu Özbek Z, Günç Ergönül P. (2020). Optimisation of wall material composition of freeze-dried pumpkin seed oil microcapsules: interaction effects of whey protein, maltodextrin, and gum arabic by D-optimal mixture design approach. Food Hydrocoll 107:105909.
-
- Allison SD, Molina MdC, Anchordoquy TJ. (2000). Stabilization of lipid/DNA complexes during the freezing step of the lyophilization process: the particle isolation hypothesis. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 1468:127–38. - PubMed
-
- Buckton G, Beezer AE. (1992). The relationship between particle size and solubility. Int J Pharm 82:R7–R10.
-
- Bulcão RP, Freitas FA, Venturini CG, et al. (2013). Acute and subchronic toxicity evaluation of poly(ε-caprolactone) lipid-core nanocapsules in rats. Toxicol Sci 132:162–76. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
