Small but Mighty-The Emerging Role of snoRNAs in Hematological Malignancies
- PMID: 34842767
- PMCID: PMC8629011
- DOI: 10.3390/ncrna7040068
Small but Mighty-The Emerging Role of snoRNAs in Hematological Malignancies
Abstract
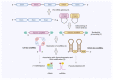
Over recent years, the long known class of small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) have gained interest among the scientific community, especially in the clinical context. The main molecular role of this interesting family of non-coding RNAs is to serve as scaffolding RNAs to mediate site-specific RNA modification of ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs) and small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs). With the development of new sequencing techniques and sophisticated analysis pipelines, new members of the snoRNA family were identified and global expression patterns in disease backgrounds could be determined. We will herein shed light on the current research progress in snoRNA biology and their clinical role by influencing disease outcome in hematological diseases. Astonishingly, in recent studies snoRNAs emerged as potent biomarkers in a variety of these clinical setups, which is also highlighted by the frequent deregulation of snoRNA levels in the hema-oncological context. However, research is only starting to reveal how snoRNAs might influence cellular functions and the connected disease hallmarks in hematological malignancies.
Keywords: leukemia; ncRNA; ribosome function; snoRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Reddy R., Busch H. Small Nuclear RNAs: RNA Sequences, Structure, and Modifications. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 1988.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

