Nd:YAG fourth harmonic (266-nm) generation for corneal reshaping procedure: An ex-vivo experimental study
- PMID: 34843558
- PMCID: PMC8629266
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0260494
Nd:YAG fourth harmonic (266-nm) generation for corneal reshaping procedure: An ex-vivo experimental study
Abstract
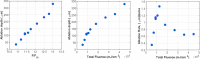
Corneal reshaping is a common medical procedure utilized for the correction of different vision disorders relying on the ablation effect of the UV pulsed lasers, especially excimer lasers (ArF) at 193 nm. This wavelength is preferred in such medical procedures since laser radiation at 193 nm exhibits an optimum absorption by corneal tissue. However, it is also significantly absorbed by the water content of the cornea resulting in an unpredictability in the clinical results, as well as the high service and operation cost of the commercial ArF excimer laser device. Consequently, other types of solid-state UV pulsed lasers have been introduced. The present work investigates the ablation effect of solid-state laser at 266 nm in order to be utilized in corneal reshaping procedures. Different number of pulses has been applied to Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) and ex-vivo rabbit cornea to evaluate the ablation effect of the produced laser radiation. PMMA target experienced ellipse-like ablated areas with a conical shape in the depth. The results revealed an almost constant ablation area regardless the number of laser pulses, which indicates the stability of the produced laser beam, whereas the ablation depth increases only with increasing the number of laser pulses. Examination of the ex-vivo cornea showed a significant tissue undulation, minimal thermal damage, and relatively smooth ablation surfaces. Accordingly, the obtained 266-nm laser specifications provide promising alternative to the traditional 193-nm excimer laser in corneal reshaping procedure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures







References
-
- Markolf NH. Laser-Tissue Interactions: Fundamentals and Applications. Germany: Springer; 2007.
-
- Hu L, Huang Y, Lin M. Excimer Laser and Femtosecond Laser in Ophthalmology. High Energy and Short Pulse Lasers. Intech; 2016. doi: 10.5772/64238 - DOI
-
- Hamdy O, Alsharafi SS, Hassan MF, Eldib A, Solouma NH. A multi-spot laser system for retinal disorders treatment: Experimental study. Opt—Int J Light Electron Opt. 2019;185: 609–613. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2019.03.158 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

