Individual dairy cow identification based on lightweight convolutional neural network
- PMID: 34843562
- PMCID: PMC8629223
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0260510
Individual dairy cow identification based on lightweight convolutional neural network
Erratum in
-
Correction: Individual dairy cow identification based on lightweight convolutional neural network.PLoS One. 2024 Jul 11;19(7):e0307252. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0307252. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38990807 Free PMC article.
Abstract
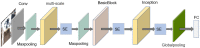
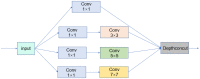
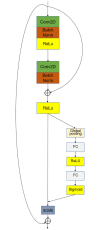
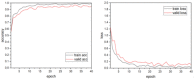
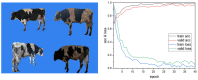
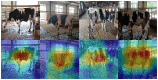
In actual farms, individual livestock identification technology relies on large models with slow recognition speeds, which seriously restricts its practical application. In this study, we use deep learning to recognize the features of individual cows. Alexnet is used as a skeleton network for a lightweight convolutional neural network that can recognise individual cows in images with complex backgrounds. The model is improved for multiple multiscale convolutions of Alexnet using the short-circuit connected BasicBlock to fit the desired values and avoid gradient disappearance or explosion. An improved inception module and attention mechanism are added to extract features at multiple scales to enhance the detection of feature points. In experiments, side-view images of 13 cows were collected. The proposed method achieved 97.95% accuracy in cow identification with a single training time of only 6 s, which is one-sixth that of the original Alexnet. To verify the validity of the model, the dataset and experimental parameters were kept constant and compared with the results of Vgg16, Resnet50, Mobilnet V2 and GoogLenet. The proposed model ensured high accuracy while having the smallest parameter size of 6.51 MB, which is 1.3 times less than that of the Mobilnet V2 network, which is famous for its light weight. This method overcomes the defects of traditional methods, which require artificial extraction of features, are often not robust enough, have slow recognition speeds, and require large numbers of parameters in the recognition model. The proposed method works with images with complex backgrounds, making it suitable for actual farming environments. It also provides a reference for the identification of individual cows in images with complex backgrounds.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




References
-
- Oliveira D A B, Pereira L G R, Bresolin T, Ferreira R. E. P., & Drea J. R. R. A Review of Deep Learning Algorithms for Computer Vision Systems in Livestock. Livestock Science, 2021;104700.
-
- Beibei Xu, Wensheng Wang, Leifeng Guo, & Guipeng Chen. Research progress and Prospect of cattle identification based on Contactless. China Agricultural Science and technology Herald, 2020;22 (7): 11
-
- Dongjian He, Dong Liu, & Kaixuan Zhao. Research progress on intelligent perception and behaviour detection of animal information in precision animal husbandry. Journal of agricultural machinery, 2016;47 (5), 231–244
-
- Yukun Sun, Yujie Wang, Pengju Huo, Ziqi Cui, & Yonggen Zhang. Research progress on cow individual recognition methods and their applications. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2019;24 (12), 62–70
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

