Optimised versus standard dosing of vancomycin in infants with Gram-positive sepsis (NeoVanc): a multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 2b, non-inferiority trial
- PMID: 34843669
- PMCID: PMC7614674
- DOI: 10.1016/S2352-4642(21)00305-9
Optimised versus standard dosing of vancomycin in infants with Gram-positive sepsis (NeoVanc): a multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 2b, non-inferiority trial
Abstract
Background: Vancomycin is the most widely used antibiotic for neonatal Gram-positive sepsis, but clinical outcome data of dosing strategies are scarce. The NeoVanc programme comprised extensive preclinical studies to inform a randomised controlled trial to assess optimised vancomycin dosing. We compared the efficacy of an optimised regimen to a standard regimen in infants with late onset sepsis that was known or suspected to be caused by Gram-positive microorganisms.
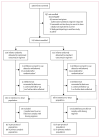
Methods: NeoVanc was an open-label, multicentre, phase 2b, parallel-group, randomised, non-inferiority trial comparing the efficacy and toxicity of an optimised regimen of vancomycin to a standard regimen in infants aged 90 days or younger. Infants with at least three clinical or laboratory sepsis criteria or confirmed Gram-positive sepsis with at least one clinical or laboratory criterion were enrolled from 22 neonatal intensive care units in Greece, Italy, Estonia, Spain, and the UK. Infants were randomly assigned (1:1) to either the optimised regimen (25 mg/kg loading dose, followed by 15 mg/kg every 12 h or 8 h dependent on postmenstrual age, for 5 ± 1 days) or the standard regimen (no loading dose; 15 mg/kg every 24 h, 12 h, or 8 h dependent on postmenstrual age for 10 ± 2 days). Vancomycin was administered intravenously via 60 min infusion. Group allocation was not masked to local investigators or parents. The primary endpoint was success at the test of cure visit (10 ± 1 days after the end of actual vancomycin therapy) in the per-protocol population, where success was defined as the participant being alive at the test of cure visit, having a successful outcome at the end of actual vancomycin therapy, and not having a clinically or microbiologically significant relapse or new infection requiring antistaphylococcal antibiotics for more than 24 h within 10 days of the end of actual vancomycin therapy. The non-inferiority margin was -10%. Safety was assessed in the intention-to-treat population. This trial is registered at ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02790996).
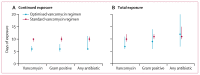
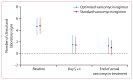
Findings: Between March 3, 2017, and July 29, 2019, 242 infants were randomly assigned to the standard regimen group (n=122) or the optimised regimen group (n=120). Primary outcome data in the per-protocol population were available for 90 infants in the optimised group and 92 in the standard group. 64 (71%) of 90 infants in the optimised group and 73 (79%) of 92 in the standard group had success at test of cure visit; non-inferiority was not confirmed (adjusted risk difference -7% [95% CI -15 to 2]). Incomplete resolution of clinical or laboratory signs after 5 ± 1 days of vancomycin therapy was the main factor contributing to clinical failure in the optimised group. Abnormal hearing test results were recorded in 25 (30%) of 84 infants in the optimised group and 12 (15%) of 79 in the standard group (adjusted risk ratio 1·96 [95% CI 1·07 to 3·59], p=0·030). There were six vancomycin-related adverse events in the optimised group (one serious adverse event) and four in the standard group (two serious adverse events). 11 infants in the intention-to-treat population died (six [6%] of 102 infants in the optimised group and five [5%] of 98 in the standard group).
Interpretation: In the largest neonatal vancomycin efficacy trial yet conducted, no clear clinical impact of a shorter duration of treatment with a loading dose was demonstrated. The use of the optimised regimen cannot be recommended because a potential hearing safety signal was identified; long-term follow-up is being done. These results emphasise the importance of robust clinical safety assessments of novel antibiotic dosing regimens in infants.
Funding: EU Seventh Framework Programme for research, technological development and demonstration.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests PTH is a member of the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence neonatal infection guideline development group. LR is an employee of Therakind. DD obtained a PhD that was funded by Fondazione Penta; the capacity and remit of this PhD was independent and unrelated to involvement with NeoVanc. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An optimised dosing regimen versus a standard dosing regimen of vancomycin for the treatment of late onset sepsis due to Gram-positive microorganisms in neonates and infants aged less than 90 days (NeoVanc): study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2020 Apr 15;21(1):329. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-4184-8. Trials. 2020. PMID: 32293527 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of cefiderocol or best available therapy for the treatment of serious infections caused by carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative bacteria (CREDIBLE-CR): a randomised, open-label, multicentre, pathogen-focused, descriptive, phase 3 trial.Lancet Infect Dis. 2021 Feb;21(2):226-240. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30796-9. Epub 2020 Oct 12. Lancet Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 33058795 Clinical Trial.
-
Cadazolid for the treatment of Clostridium difficile infection: results of two double-blind, placebo-controlled, non-inferiority, randomised phase 3 trials.Lancet Infect Dis. 2019 Mar;19(3):265-274. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30614-5. Epub 2019 Jan 29. Lancet Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 30709665
-
Antibiotic regimens for late-onset neonatal sepsis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 May 8;5(5):CD013836. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013836.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33998665 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Physicochemical Characteristics of Antimicrobials and Practical Recommendations for Intravenous Administration: A Systematic Review.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Aug 19;12(8):1338. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12081338. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37627758 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Safe and effective use of vancomycin.Aust Prescr. 2025 Apr;48(2):54-59. doi: 10.18773/austprescr.2025.013. Aust Prescr. 2025. PMID: 40343139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibiotics, Analgesic Sedatives, and Antiseizure Medications Frequently Used in Critically Ill Neonates: A Narrative Review.Children (Basel). 2024 Jul 18;11(7):871. doi: 10.3390/children11070871. Children (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39062320 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expert review of CLABSI prevention in the NICU: supporting the transition of investigational drugs into clinical practice.Eur J Pediatr. 2025 Jul 19;184(8):492. doi: 10.1007/s00431-025-06329-9. Eur J Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40682607 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fleischmann-Struzek C, Goldfarb DM, Schlattmann P, Schlapbach LJ, Reinhart K, Kissoon N. The global burden of paediatric and neonatal sepsis: a systematic review. Lancet Respir Med. 2018;6:223–30. - PubMed
-
- Cailes B, Kortsalioudaki C, Buttery J, et al. Epidemiology of UK neonatal infections: the neonIN infection surveillance network. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2018;103:F547–53. - PubMed
-
- Alshaikh B, Yee W, Lodha A, Henderson E, Yusuf K, Sauve R. Coagulase-negative staphylococcus sepsis in preterm infants and long-term neurodevelopmental outcome. J Perinatol. 2014;34:125–29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

