Wave comparisons of clinical characteristics and outcomes of COVID-19 admissions - Exploring the impact of treatment and strain dynamics
- PMID: 34844145
- PMCID: PMC8608665
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcv.2021.105031
Wave comparisons of clinical characteristics and outcomes of COVID-19 admissions - Exploring the impact of treatment and strain dynamics
Abstract
Objectives: Dexamethasone has now been incorporated into the standard of care for COVID-19 hospital patients. However, larger intensive care unit studies have failed to show discernible improvements in mortality in the recent wave. We aimed to investigate the impacts of these factors on disease outcomes in a UK hospital study.
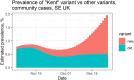
Methods: This retrospective observational study reports patient characteristics, interventions and outcomes in COVID-19 patients from a UK teaching hospital; cohort 1, pre 16th June-2020 (pre-dexamethasone); cohort 2, 17th June to 30th November-2020 (post-dexamethasone, pre-VOC 202,012/01 as dominant strain); cohort 3, 1st December-2020 to 3rd March-2021 (during establishment of VOC202012/01 as the dominant strain).
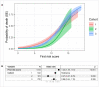
Results: Dexamethasone treatment was more common in cohorts 2 and 3 (42.7% and 51.6%) compared with cohort 1 (2.5%). After adjusting for risk, odds of death within 28 days were 2-fold lower in cohort 2 vs 1 (OR:0.47,[0.27,0.79],p = 0.006). Mortality was higher cohort 3 vs 2 (20% vs 14%); but not significantly different to cohort 1 (OR: 0.86,[0.64, 1.15],p = 0.308).
Conclusions: The real world finding of lower mortality following dexamethasone supports the published trial evidence and highlights ongoing need for research with introduction of new treatments and ongoing concern over new COVID-19 variants.
Keywords: COVID-19 variants; COVID-19 waves; Dexamethasone.
Copyright © 2021. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures
References
-
- Wilkinson T., Dixon R., Page C., Carroll M., Griffiths G., Ho Ll-P, et al. ACCORD: a multicentre, seamless, phase 2 adaptive randomisation platform study to assess the efficacy and safety of multiple candidate agents for the treatment of COVID-19 in hospitalised patients: a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials. 2020;21(1):691. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Monk P.D., Marsden R.J., Tear V.J., Brookes J., Batten T.N., Mankowski M., et al. Safety and efficacy of inhaled nebulised interferon beta-1a (SNG001) for treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021;9(2):196–206. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

