The dynamic changes of HBV quasispecies diversity in infancy after immunoprophylaxis failure: a prospective cohort study
- PMID: 34844612
- PMCID: PMC8628401
- DOI: 10.1186/s12985-021-01707-9
The dynamic changes of HBV quasispecies diversity in infancy after immunoprophylaxis failure: a prospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: Previous works have observed that younger infants with chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection are more responsive to antiviral treatment. However, the underlying mechanism remains unclear. In this study, the dynamic changes of HBV quasispecies in infants with immunoprophylaxis failure were investigated to provide virological explanations for clinical management on infantile antiviral therapy.
Methods: Thirteen 7-month-old infants with immunoprophylaxis failure and their mothers were enrolled from a prospective cohort, and 8 of them were followed up to 3 years old. The sequences of HBV quasispecies were analyzed by the full-length genome clone-based sequencing, and compared among mothers and their infants at different ages.
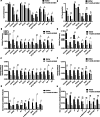
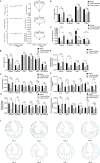
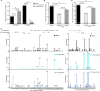
Results: The results revealed that the complexity, mutation frequency and genetic distance of HBV quasispecies decreased significantly at full-length, partial open reading frames and regulatory regions of HBV genome at nucleotide level in 7-month-old infants comparing with their mothers, whereas increased significantly to near the maternal level when infants grew up to 3 years old. Furthermore, similar changes were also found in Core, PreS2, RT and P regions of HBV genome at amino acid level, especially for potential NAs-resistant mutants in RT region and immune-escape mutants in Core and PreS2 regions.
Conclusions: This study uncovered the evolution of HBV quasispecies in infancy after mother-to-child transmission, which may provide the virological evidence for explaning that younger children are more responsive to antiviral therapy.
Keywords: Hepatitis B virus; Immunoprophylaxis failure; Infantile antiviral therapy; Mother-to-child transmission; Quasispecies.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Characteristic of HBV Quasispecies Is Related to Occult HBV Infection of Infants Born to Highly Viremic Mothers.Viruses. 2024 Jul 9;16(7):1104. doi: 10.3390/v16071104. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39066265 Free PMC article.
-
Quasispecies characteristic in "a" determinant region is a potential predictor for the risk of immunoprophylaxis failure of mother-to-child-transmission of sub-genotype C2 hepatitis B virus: a prospective nested case-control study.Gut. 2020 May;69(5):933-941. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-318278. Epub 2019 Aug 24. Gut. 2020. PMID: 31446427 Free PMC article.
-
Quasispecies characters of hepatitis B virus in immunoprophylaxis failure infants.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2018 Jun;37(6):1153-1162. doi: 10.1007/s10096-018-3235-5. Epub 2018 Apr 8. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 29629487
-
Immunoprophylaxis failure against vertical transmission of hepatitis B virus in the Chinese population: a hospital-based study and a meta-analysis.Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2014 Sep;33(9):897-903. doi: 10.1097/INF.0000000000000315. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2014. PMID: 25361021 Review.
-
Antivirals for prevention of hepatitis B virus mother-to-child transmission in human immunodeficiency virus positive pregnant women co-infected with hepatitis B virus.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jun 12;6(6):CD013653. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013653.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37306558 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Functional Cure of Chronic Hepatitis B with Antiviral Treatment in Children having High-level Viremia and Normal or Mildly Elevated Serum Aminotransferase.J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2023 Oct 28;11(5):1011-1022. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2023.00014. Epub 2023 Apr 10. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 37577220 Free PMC article.
-
Why is the functional cure rate of young children with chronic hepatitis B receiving antiviral therapy considerably high?Hepatol Int. 2024 Feb;18(1):296-298. doi: 10.1007/s12072-023-10597-8. Epub 2023 Oct 31. Hepatol Int. 2024. PMID: 37907721 No abstract available.
-
HBx 128-133 Deletion Affecting HBV Mother-to-Child Transmission Weakens HBV Replication via Reducing HBx Level and CP/ENII Transcriptional Activity.Viruses. 2022 Aug 26;14(9):1887. doi: 10.3390/v14091887. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36146694 Free PMC article.
-
The Characteristic of HBV Quasispecies Is Related to Occult HBV Infection of Infants Born to Highly Viremic Mothers.Viruses. 2024 Jul 9;16(7):1104. doi: 10.3390/v16071104. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39066265 Free PMC article.
-
Gene-Editing and RNA Interference in Treating Hepatitis B: A Review.Viruses. 2023 Dec 8;15(12):2395. doi: 10.3390/v15122395. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 38140636 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

