The dark proteome: translation from noncanonical open reading frames
- PMID: 34844857
- PMCID: PMC8934435
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tcb.2021.10.010
The dark proteome: translation from noncanonical open reading frames
Abstract
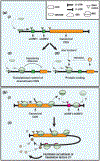
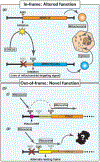
Omics-based technologies have revolutionized our understanding of the coding potential of the genome. In particular, these studies revealed widespread unannotated open reading frames (ORFs) throughout genomes and that these regions have the potential to encode novel functional (micro-)proteins and/or hold regulatory roles. However, despite their genomic prevalence, relatively few of these noncanonical ORFs have been functionally characterized, likely in part due to their under-recognition by the broader scientific community. The few that have been investigated in detail have demonstrated their essentiality in critical and divergent biological processes. As such, here we aim to discuss recent advances in understanding the diversity of noncanonical ORFs and their roles, as well as detail biologically important examples within the context of the mammalian genome.
Keywords: CRISPR; microproteins; noncanonical ORFs; ribosome profiling; short ORFs; translation.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration on Interests∣
J.S.W. declares outside interest in 5 AM Venture, Amgen, Chroma Medicine, KSQ Therapeutics, Maze Therapeutics, Tenaya Therapeutics, Tessera Therapeutics, Third Rock Ventures, and Velia Therapeutics. J.C. consults for Velia Therapeutics.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

